 ISSN : 1598-2939
ISSN : 1598-2939

Osteoporosis is characterized by a loss of bone density and strength resulting in increased risk of fracture. One promising method for preventing fractures is participation in bone-strengthening physical activity. While the importance of mechanical loading for bone health is understood, assessment strategies are limited. Most researchers measure metabolic loads rather than mechanical loads, but not all activities that improve metabolic health increase bone strength. The osteogenic properties of physical activity (e.g., magnitude of the load, rate at which the load is applied, dynamic and odd nature of the load, duration of loading session, and breaks between sessions) have not traditionally been directly measured in health outcomes and surveillance research. The lack of research in this area has slowed our understanding of exactly what dose of bone-strengthening physical activity to recommend to the public as well as how to prescribe exercise to reduce the risk of fractures. To understand the influence of mechanical loading on bone adaptation, measurement methods must capture multiple physical activity dimensions (intensity, frequency, and time). Advancements in accelerometer technology now allow for the measurement of these dimensions. It is time that the lessons learned from using accelerometers in cardiometabolic health outcomes research be applied to musculoskeletal health.

The purpose of this study was to test a protocol for establishing collective technical and tactical performance goals in elite men’s volleyball. The participants were a professional volleyball team. The period of study was one entire season. A baseline was established in the first half of the season, and the intervention was carried out in the second half of the season. The intervention involved the use of seven collective performance goals for monitoring the team in competitions. The variables studied were: the achievement of the collective performance goals that were established; the game phase; the result of the set; and the players’, coaches’, and psychologist’s perception of the use of the performance goals and the poster. The team slightly increased the number of goals achieved per game in the intervention period. There was a significant reduction in serve errors and a significant increase in block contacts. The intervention increased the players’ engagement with the team, although there were differences in opinion about the effect on the different players. The intervention improved the players' understanding of the match. The effects of the goal-setting and the poster were positively perceived, due to helping the players to understand their needs and the aspects to improve.

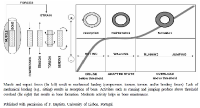
Purpose: To examine the concurrent validity of the T-REX accelerometer assessing physical activity against indirect calorimetry (oxygen uptake) and two different accelerometers (Actical and ActiGraph). Methods: Fifty healthy volunteers (25 men, age 23.5 ± 1.7 years; 25 women, age 22.4 ± 2.0 years) participated in tests using treadmill protocol. They walked or ran on a treadmill at four different speeds (4, 6, 8, and 10 km∙h⁻1 for men and 4, 6, 7.5, and 9 km∙h⁻1 for women) for 5 min at each speed. During the test, the T-REX (Taewoong Medical Co., Ltd., Korea) was attached at five locations on the body (ankle, arm, chest, waist, and wrist), the Actical was attached at two locations (waist and chest), and the ActiGraph was worn at the waist. Oxygen uptake (VO2) was measured using a portable device during exercise, and metabolic equivalents (METs) were calculated. The validity of the T-REX was assessed using Pearson correlations and Bland–Altman plots. Results: There were strong associations between T-REX and VO2 in men (r = 0.92–0.95) and women (r = 0.83–0.91) on the treadmill test (p<0.001). Associations between the T-REX and two different accelerometers (Actical and ActiGraph) were also strong (r = 0.89–0.98). Similar associations were also observed between VO2 and Actical (r = 0.87–0.95) and between VO2 and ActiGraph (r = 0.85–0.87). In the Bland–Altman plots, there were no statistical differences between VO2 and five T-REX sensor locations in both men and women (all p>0.05). Conclusion: The T-REX has a high concurrent validity with VO2 in assessing energy expenditure in men and women. This device might be an alternative to conventional accelerometers.

Managing human capital in an effective manner is always a challenge for sport managers. The purpose of the study was to examine the relationships among perceived support, collectivism, affective commitment, work effort, and intention to leave among sport instructors across the United States. The data were collected from 379 ACSM certified sport instructors using online questionnaire. The results showed that perceived support, which is represented by coworker support, supervisor support, and organizational support, and collectivism had a significant impact on affective commitment explaining 75.0% and 13.2% of the variances respectively. In addition, affective commitment explained 19.0% of the variance in work effort and 61.9% of the variance in intention to leave. This study significantly contributes to the existing body of knowledge in sport management literature and provides meaningful guidance to sport managers on how to retain valuable employees and elicit the best work effort they could offer.
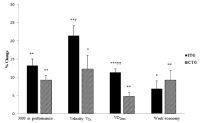
This study evaluates and compares the effect on endurance performance between high intensity interval training (ITG) and low intensity, longer-lasting training (CTG) with twice longer training time than ITG. We selected 22 healthy, non-smoking young men and women in a randomised trial to undertake either low intensity continuous training at 75% of maximal heart rate (HRmax) for 75 minutes or high intensity interval training at 90–95% HRmax, to undertake training either low intensity or high intensity three times a week for eight weeks. Performance times for running 3000 metres improved in both groups. Effect size between groups was 0.95 in favour of the ITG. Maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), running economy (RE) and speed at ventilatory threshold (VTh) improved in both groups. VO2max and speed at VTh improved significantly more in the ITG. RE did not differ between the groups. The result of this study indicate that high intensity training is more effective and time efficient in improving performance in recreational runners than low intensity continuous training.

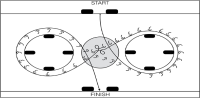
The purpose of this study was to examine whether there exists a correlation between changes in off-season power and changes in in-season skating performance among young ice hockey players. Eighteen elite male players (15.8 ± 0.9) completed on-ice and off-ice performance tests on three separate occasions during a season. Forward and backward skating speed, on-ice agility test, 36 m sprint running performance, broad jump and countermovement jump (CMJ) were included. Off-season improvements in 36 m sprint running performance (r = 0.57, P= 0.02) and changes in broad jump (r = -0.48, P= 0.04) where significantly correlated with in-season improvements in forward skating speed. However, off-season changes in 36 m sprint running performance and jump ability were not significantly correlated with in-season improvements in backward skating speed or agility. These results suggest that an off-season training program that includes sprints and horizontal jumping exercises may have a positive effect on hockey players’ linear skating speed.

The main purposes of the current study were 1) to understand the perceptions of consumers toward congruency levels for a placed brand based on the type of movie and gender of endorser and 2) to examine the relationship between consumers’ perceptions of congruency and purchase intention to have a successful sport media sponsorship. A total of 200 participants completed the questionnaires. The results revealed consumers had higher perceptions of congruency for a sportswear brand placed in a sports program than in a non-sports program. This study also found the positive association between congruency and purchase intention.
The environment fostered by a coach can be an extremely important variable in an athlete’s or team’s drive towards success. Choices about whether perceived competence is seen as predominantly self-referenced, task-mastery oriented, other-referenced or performance-avoidance oriented are very important. Also, the extent to which the coach nourishes group-oriented or individual-oriented competence motivation in team sports is important. This study set out to analyse questions regarding competence motivations in the elite sporting landscape of Singapore. The results suggest that four basic competence needs should be considered highly by coaches in this context. In both team and individual sports, the following are important: the development of an athlete’s feelings of self-worth through awareness of competence; athletes should be reminded that they are perceived as competent by other competing athletes; and coaches should make explicit that athletes are competent and that the spectators of a match are enjoying their play. The final basic competence relates solely to team sports: the importance of the team’s performance or competence above all else. It is hoped that findings from this study might be useful to coaches and transferable to other Asian contexts.
The aim of this review was to assess the influence of habitual physical activity upon the risk of developing renal cancer. Some benefit might be anticipated through favourable effects of exercise upon immune function, oxidative stress, obesity, and the resulting modulation of hormones influencing the growth of cancerous cells. A systematic search of the Ovid/Medline data-base from 1996 to August 20th 2016 was supplemented by a review of reference lists and personal files. A total of 27 unique cohort and case-control studies were found, many covering both occupational and leisure activity. No papers pointed to any increase of risk for individuals with an active lifestyle, but only 6 of 13 cohort and 6 of 14 case-control studies showed any statistically significant association between greater physical activity and lower risk. Moreover, even in these articles, benefit was usually confined to a specific subset of the original sample identified post-hoc. The overall weighted risk ratio for active individuals was 0.88 in cohort and 0.93 in case-control studies, but risk ratios became 0.96 and 0.94 on omitting analyses that did not include important co-variates such as obesity and smoking. This suggests that habitual physical activity reduces the risk of renal cancer largely through a modulation of these variables. Problems that must be addressed in future investigations of this topic include finding populations that include an adequate number of cases of renal cancer, making a better (and preferably objective) categorization of physical activity, and handling the influence of co-variates in a more systematic fashion. There is also scope for prospective trials in humans, and further studies in animal models of renal carcinoma.
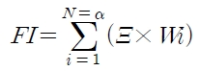
This study recounts what influences sports athlete reputation. As social media have become more widespread, athlete’s non-sport-related activities can be accessed almost instantly. This change in the media environment requires sports athletes not only to attend to their sporting ability, but also to systematically manage non-sport factors in order to maintain and improve their brand values and reputations. In order to collect factors constructing sports athlete reputation, a pre-study including an open-ended survey based on free association, analysis of media reports, and consultations from sports experts was conducted. The pre-study process resulted in a final number of 44 items for use in the study. In the main survey, 452 panelists were collected through an on-line survey. To verify the 44 items of sports athletes’ reputations Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) was conducted. As a result of EFA, 21 items were finally selected and grouped into six factors: a) game results; b) management of playing capability; c) personal character; d) external appeal; e) sportsmanship, and f) management of privacy. The results from this study also suggest that game results are the most important factor influencing sports athletes’ reputations. Management of playing capability and sportsmanship are considered more important than are personal character, external appeal, or privacy management. It is expected that the result of this study would help corporations to develop strategic analysis for sports athletes’ reputation.
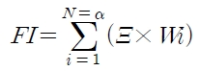
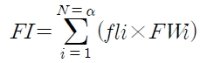
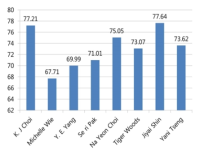
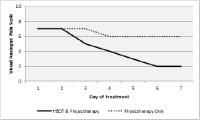
The study investigated the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) on ankle functions of patients with grade I ankle sprains. Two male patients with grade I acute ankle sprain were categorised into either combined HBOT and physiotherapy or physiotherapy only groups. Pain index and ankle isokinetic peak torque, time to peak torque and average power were evaluated on the first day of the injury before the commencement of the therapy and after a week of the therapy. The HBOT was administered with 2.5 ATA, 60 min per session, a session per day for five consecutive days. Standard physiotherapy was prescribed for both patients for a week. The data were analysed by descriptive statistics and percentage differences. Combined HBOT and physiotheraphy treatment was more effective in reducing pain compared to physiotherapy only. Isokinetic ankle strength improved in both patients from pre-test to post-test. However, the patient administered with combined HBOT and physiotherapy showed a higher percentage difference in isokinetic peak torque and time to peak torque compared to the other patient. Additional HBOT over the standardised physiotherapy in patient with grade I ankle sprain may help in reducing the pain sensation quicker, eliciting faster recovery, and improving isokinetic ankle strength.

The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of performance routine on competitive state anxiety, psychological skills and perceived performance of Taekwondo form players. The participants were composed of three women Taekwondo form players in university. The instruments of this study were composed of TOPS (Test of Performance Strategy Inventory), Revised Competitive State Anxiety-2 (Revised CSAI-2), Competition reflection Questionnaires, and perceived performance inventory. The performance routine program for Taekwondo form players was the broad routine (behavioral routine, cognitive routine), mistake coping routine, unexppected condition coping routine. 8 session performance routine program was applied to participants about 50-minute session (1 times session a week) every week. The results were as follows. Firstly, performance routine program decreased cognitive anxiety and somatic anxiety intensity but increased self-confidence intensity of Taekwondo form players. Also, performance routine program positively changed direction of cognitive anxiety, somatic anxiety and self-confidence of Taekwondo form players. Secondly, performance routine program increased self-talk, relaxation, emotion control level of Taekwondo form players. Thirdly, performance routine program enhanced perceived performance of Taekwondo form players. Lastly, qualitative data such as interview examined that performance routine program positively impacted positive thinking, competitive state anxiety, psychological skills and perceived performance of Taekwondo form players.
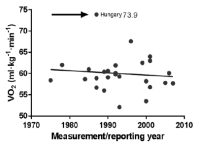
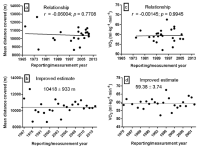
The present review investigate whether aerobic capacity of elite male soccer players has changed over the past 30-40 years, and sought to establish an improved estimate of aerobic capacity based on results reported in the literature. A systematic review of manuscripts reporting the match distance covered and/or the VO2max of elite male soccer players was performed. Eighteen studies (published between 1967 and 2010) reporting the total distance covered and representing 14 countries (3,833 players), and 25 studies (published between 1975 and 2012) reporting VO2max and representing 22 countries (1,921 players) were selected for analysis. Little, if any, relationship existed between the mean match play distance covered/VO2max and the year of measurement/reporting. An improved estimate of the match play distance covered was calculated as 10,418 m with a pooled standard deviation of ± 933 m (95% confidence interval [CI] = 10,053 – 10,783 m) and a maximum mean of 12,650 m and minimum of 8,638 m. In addition, the improved estimate of the VO2max was calculated as 59.38 mL∙kg⁻1∙min⁻1, with a pooled standard deviation of ± 3.74 mL∙kg⁻1∙min⁻1 (95% CI = 57.99 – 60.78 mL∙kg⁻1∙min⁻1) and a maximum mean of 67.6 mL∙kg⁻1∙min⁻1, and a minimum of 52.1 mL∙kg⁻1∙min⁻1. The results suggest that distance covered and VO2max in elite male soccer players have been stable over the period from 1967 to 2012 and that aerobic metabolism is the major source of energy during the match. Thus, soccer players must possess a minimum aerobic capacity to cover the total match distances and to recover from high-intensity action.

The main aim of the present study was to investigate any effects from attention training techniques (ATT) on junior elite athletes’ perceived level of stress, perceived performance in sports, and perceived performances in school. Fifty-eight athletes from various sports such as alpine skiing, cross-country skiing, handball, biathlon, ski-jumping and Nordic combined completed an ATT training program over a period of 12 weeks. A pre-test/post-test control group design was used to investigate any effects from the ATT training program. The results from this study showed that there was a decreased level of perceived stress, and a positive change in perceived performances in sports, but not in school performances, among the athletes in the experiment group. There were no positive changes in the control group. The implications are discussed according to the changes in the athletes’ attentional awareness and control.
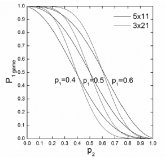
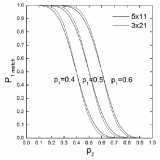
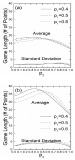
A model based on the probability of the server winning the rally was employed to evaluate the influence of the newly proposed scoring system, the best of five games of 11 points scoring system, being experimented by the Badminton World Federation on singles badminton matches. The model, based on the assumption of statistical independence on each point’s outcome, was used to generate predictions ranging from the game- and match-winning probabilities to game- and match-length statistics for matches under both the new and the current scoring system, the best of three games of 21 points. Validity of these results was checked against tournament data, four sets each for the two scoring systems, as well as previously published results, with satisfactory agreement in most cases. The results show that duration of singles matches would be reduced noticeably under the new scoring system without affecting the match outcome of the current scoring system.


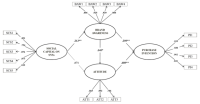
The aim of this study was to investigate how Generation Y consumers’ social capital on social network sites (SNSs) influences brand awareness and attitude towards purchase intentions for eco-friendly outdoor sportswear (EFOS). The result showed that social capital on SNSs has a positive effect on psychological perception of EFOS. Also, the perception of EFOS had not only a positive effect on attitude towards EFOS, but also directly affected purchase intention for EFOS. The outcomes of this study could offer sportswear marketers to understand Generation Y’s cognitive and behavioral involvement and to develop effective marketing strategies to promote EFOS. Therefore, Generation Y consumers’ purchase intentions can be fully stimulated.
