 ISSN : 1598-2939
ISSN : 1598-2939
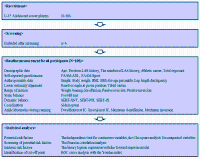
Lateral ankle sprain (LAS) is the most common injury in Korean adolescent soccer players. However, intrinsic risk factors for LAS in adolescent soccer players remain unclear. Therefore, this prospective cohort study aimed to identify intrinsic risk factors for LAS in Korean adolescent soccer players. This study included 100 adolescent soccer players (age=13.21±0.95 years, height=1.62±0.09 m, weight=53.37±9.54 kg, BMI-for-age percentile=63.78±20.89%, athletic career=3.95±1.96 years). Baseline measurements were performed in the preseason, and the injury surveillance on LAS was conducted for 1 year. Independent variables included participants’ demographic and anthropometric data, self-reported questionnaire, lower extremity alignments, range of motion, static, and dynamic balance, coordination, and ankle kinematics during running. Independent t-test and Chi-square analysis were used for potential risk factors, which were imported to the binary logistic regression to identify intrinsic risk factors for LAS. Data on intrinsic risk factors identified by the logistic regression were analyzed using the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis to determine a cutoff point of each variable. In this study, age, body mass index, previous LAS history, the number of LAS history, and maximum dorsiflexion and inversion during the stance phase of running were potential risk factors for LAS. Our major findings showed that decreased dorsiflexion and increased inversion at initial contact during running significantly affected LAS occurrence in Korean adolescent soccer players. Considering our major findings, to prevent LAS in adolescent soccer players, gait training must not be overlooked and should be included in warm-up sessions.

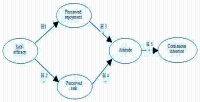
The exponential growth in engagement with extreme sports in recent decades has surpassed our understanding of the perceptions and personal experiences of those individuals who participated. This research explores the relationship between self-efficacy, perceived enjoyment, perceived risk, attitude toward behavior, and continuance intention within the framework of the theory of planned behavior. The study collected data from 193 parkour enthusiasts who associated with Chinese amateur parkour clubs. Hypotheses were verified using structural equation modeling using AMOS 26.0. The results demonstrate notable associations across all categories, however, the hypothesis that perceived risk will influence attitude toward behavior was not supported. The study concludes with discussions on the implications for scholars and practitioners and suggestions for future research.

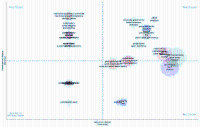
The current study aims to highlight the current trends in the literature on sport governance by applying a bibliometric review of papers on sport governance topics published in the Web of Science database. This study reviews 230 Web of Science-indexed journal articles on sport governance and analyzed the data using bibliometric analytic tools such as thematic mapping and co-citation analysis. The findings reveal a notable increase in research on sport governance over time. Over the past three decades, diverse topics within sport governance have been explored, with a significant emphasis on national sport organizations, corruption, gender, leadership, volunteer boards, and collaborative governance. The study identifies gender dynamics and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) as emerging key research areas. The results not only contribute to our understanding of current sport governance literature but also point towards potential future research directions. These include the development of a comprehensive framework, exploration of outcome-related governance principles, and the application of governance principles to local and non-European sport organizations and systems.


Physical activity in early childhood plays a crucial role in the holistic development of young children. However, challenges persist in the effective implementation of early childhood physical education (ECPE) due to the lack of specialized expertise among early childhood teachers. This study aimed to identify the essential components of the teaching competency required for ECPE through a Delphi survey approach. A panel of experts categorized teaching competency into four core areas: physical activity education, understanding learners, professional development, and environmental management. This study highlights the importance of reflective professionalism, safety management, and creating a positive learning environment. The findings offer valuable guidance for enhancing teacher education and professional development programs, ultimately empowering early childhood teachers to provide meaningful and effective physical activity education to young children. Further research is needed to explore how these competencies can be effectively integrated into ECPE settings.
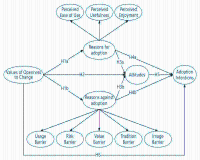
The use of digital technology in sport is an inevitable trend, but the behavioral decision-making process of sport participants using digital technology for sport participation is unclear. This study used behavioral reasoning theory to develop and validate a theoretical model that analyses participants’ behavioral cognitive decision-making by considering both reasons for adoption and against adoption and in doing so, explains sport participants’ behavioral decision-making in using digital technology for sport participation, which is a theoretical extension of existing innovation frameworks in sport management and marketing. The study found that respondents’ reasons against adoption the use of digital technology for sport participation had a greater influence on their attitudes and behavioral intentions, with perceived hedonism and barriers to use being the dominant factors in the reason for adoption and against adoption, respectively, and participants’ values significantly influencing the reasons for adoption and against adoption the use of digital technology for sport participation. This study provides unique insights for developers and related marketing promoters of digital technology applications in sport, and in expanding the impacts associated with the use of digital technology in sport, it is necessary to clarify the reasons for adoption and against adoption, and to consider the values of the participants, so that the combination of digital technology and sport can better meet the actual needs of the participants.

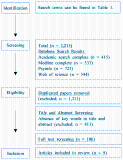
Given the barriers to physical activity (PA) that people with disabilities face, web-based PA interventions have garnered attention to promote their engagement in PA. However, previous studies have yielded inconsistent results regarding the impact of these interventions on PA among peoples with disabilities. The aim of this systematic review was to assess the effects of web-based PA interventions on PA in peoples with disabilities. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines were adopted as the framework for this review. Four databases—Academic Search Complete, Medline Complete, PsycINFO, and Web of Science—were searched, and three coders independently reviewed the retrieved studies. A total of nine studies were included in this review. These studies comprised a combined sample size of 314 participants, with 192 in the experimental groups and 122 in the control groups. The web-based interventions examined in these studies fell into four categories: 1) application-based, 2) text messaging, 3) video/phone calls, and 4) web platforms. Of the nine studies, four reported significant and positive effects on PA among people with disabilities. However, the remaining studies found no significant effects. Given these inconclusive findings, further research is warranted to ascertain the effectiveness of web-based PA interventions. Future studies should focus on identifying and addressing the barriers that participants may face in accessing these interventions.

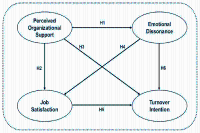
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationships among emotional dissonance, perceived organizational support, job satisfaction, and turnover intention among physical education professors in China. The population for this study consisted of physical education professors in L province, China. Convenience sampling was utilized, and a total of 192 participants participated the study. An online survey system, Tencent Questionnaire, was employed to administer the survey. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS 27.0 and AMOS 27.0, and structural equation model was employed to examine the relationships among the variables. According to the results, first, perceived organizational support has no significant effect on emotional dissonance. Second, perceived organizational support is positively related to job satisfaction. Third, perceived organizational support has no significant effect on turnover intention. Fourth, emotional dissonance is negatively related to job satisfaction. Fifth, job satisfaction has no significant effect on turnover intention. Sixth, emotional dissonance is positively related to turnover intention. Moreover, perceived organizational support was a significant predictor of job satisfaction. Additionally, emotional dissonance demonstrated a negative association with job satisfaction and a positive association with turnover intention. This is the first study to highlight the importance of emotional states and contextual factors on well-being and job-related attitudes in the physical education context.
