 ISSN : 1598-2939
ISSN : 1598-2939
An increasing number of studies have explored the relationship between exercise and cognitive function. While the majority of studies have focused on the effects of aerobic exercise, some studies have shifted their attention to other exercise modalities such as resistance exercise and Tai Chi Chuan. The purpose of this brief review is to explore the effects of aerobic exercise, resistance exercise, and Tai Chi Chuan on cognitive function by reviewing previous research on each of those exercise modalities and their relationships to cognition, including the potential mechanisms underlying those relationships. Generally speaking, a positive effect of aerobic training on cognitive function is observed. While the research evidence regarding the effects of resistance exercise and Tai Chi Chuan on cognitive function are only somewhat established, their positive trend indicates that future studies are warranted to investigate them further.
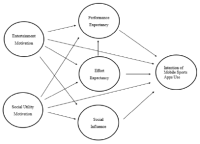
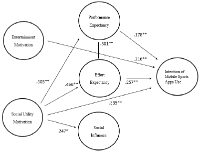
The current study was to test how the modified Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) can apply to continuance intention of mobile sports apps. As a result of survey procedures and after eliminating incomplete questionnaires, a total of 267 responses (N=267) of college students who encompasses the greatest proportion of mobile technology devices users were garnered for main analysis. The results of proposed model testing indicate that social utility (i.e., information of sports), entertainment (i.e., escape from routine), and effort expectancy (i.e., easiness to use) are important factors influencing continuance intention of mobile sports apps. This proposed test of the modified UTAUTmay contribute to develop theoretical and conceptual model in sports related technology users’ motivation and satisfaction literatures. Further theoretical and managerial implications are also discussed.

While previous research highlights the important value that sports happiness can have for athletes’ quality of life, limited research has examined the sports happiness of elite athletes. The purpose of this study was to examine the difference between Korean, Chinese, and Japanese Elite Swimming athletes’ sports happiness and, if there was any, how the result was similar and different cross-culturally/nationally. Semi-structured interviews were conducted with total 12 elite swimming athletes. Participants were both males (n = 6) and females (n = 6), who were between 19-23 years old with average 13.9 years of swimming experience. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and were analyzed with a content analysis procedure in which raw meaning units were grouped into salient themes. Athletes’ responses regarding happiness derived from this in-depth interview revealed five categories: 1) athletes’ perception of happiness. 2) happiness in everyday life 3) happiness in practice and competition situations 4) coach-athlete relationship 5) material happiness. The participants perceived their happiness were associated with a pleasure, satisfaction and in practice and competition situation and most of athletes answered that happiness is when they have good results. But material rewards and benefits given to them cannot be seen happiness but a supporting. Social and cultural processes making these different outcomes are discussed.
Weightlifting is a sport that demands dynamic strength and power which involves a multi joint movement and whole body lifts. As an important kinetic chain involved in motions of weightlifting, previous literatures reported shoulder injuries due to muscular imbalance of shoulder rotator cuff muscles. Therefore, the study was conducted to evaluate the effects of isokinetic versus isotonic training on strength, power and muscular balance of the rotator cuff. A total of 24 state-level weightlifters were recruited and randomly assigned (gender- and weight-matched) into either isokinetic or isotonic group. However, only 19 participants successfully completed the intervention programme. Both groups went through 24 sessions of a training program three times per week for eight weeks. The intensity of training was increased progressively in terms of number of repetitions and set. Isokinetic variables of peak torque per body weight, time to peak torque, average power and external to internal rotators muscular strength ratio were recorded before and after the commencement of training and one month following the cessation of training. There was a non-statistically significant trend that indicated positive changes in the biomechanical adaptations of the rotator cuff in the isokinetic group compared to the isotonic group in terms of peak torque/body weight, time to peak torque and average power. In conclusion, both isokinetic and isotonic training specifically for rotator cuff has a potential to be proposed as an additional training among experienced weightlifters to improve their performance.
The purpose of this study was to develop and apply a team building program for a curling team through needs assessment. The participants in this study were 69 high-school, college, professional, and national curling athletes for the needs assessment, 4 sport psychologists and 2 curling experts for verifying the validity of the program, and 5 curling athletes of professional curling teams for the application of the team building program. The needs assessment data were analyzed by inductive content analysis. The team building program was developed based on the results of needs assessment, goal setting of the team building program, and a selection of activities for the team building program. The team building program was applied to five curling players for 7 sessions. Team cohesion, team efficacy, and effective communication were measured two times (i.e., pre and post) to examine the effects of team building intervention. The results of needs assessment indicated interpersonal relationship, communication, and performance were necessary factors for team building. Consequently, goals of the team building program were to improve communication and interpersonal relationships. Team building activities were selected through team building literature review and expert meetings. Secondly, the team building intervention had a positive influence on team cohesion, team efficacy, and communication. These results indicated that team building would positively contribute to team factors and team performance.
The purpose of this study was to compare physique, body composition and physical fitness 41 national ice hockey players team between forwards and defenders of the results were summarized as follow there were no statistically significant differences in all items of physique and body composition between forwards and defenders. Significiant muscular strength, cardiorespiratory endurance (maximum oxygen uptake and 20m shuttle run) (p<.05, p<.05). maximum strength, power and anaerobic power, muscle mass, body fat which are insufficient compared to foreign players. In conclusion, the national women’s ice hockey team can improve athletic performance by increasing muscular strength, muscular power, anaerobic power and muscle mass and reducing body fat. Muscular strength and cardiorespiratory endurance are important factors to distinguish between forwards and defenders when selecting and finding players.
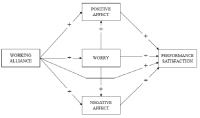
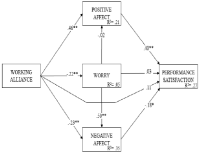
The current study aimed to explore the association between subjective performance and coach-athlete working alliance, positive and negative affect, and worry among Norwegian junior elite athletes. A sample of 358 junior elite athletes from 3 different high schools specialized in sports participated in the investigation. A theoretical model was tested, in which working alliance between coaches and athletes was expected to be associated with positive and negative affect, worry and subjective performance. Results show that this theoretical model explains 27% of the variance in subjective performance, whereas working alliance is significantly associated with positive and negative affect. Furthermore, worry, and positive and negative affect are significantly associated with subjective performance, while worry is significantly associated with negative affect. These results are discussed based on the Cognitive Activation Theory of Stress, and indicate that there are three crucial facets essential for building an effective coach-athlete relationship. These include, firstly, coaches’ abilities to establish strong emotional bonds with their athletes; secondly, coaches’ competence in setting goals that are mutually understood; and thirdly, determination of tasks which are perceived by athletes as helpful in goal attainment.


The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of structural changes on competitive balance in the Korean Professional Baseball League (KPBL). The study used standard deviation of winning percentages (SDWP) and Gini coefficient to measure competitive balance in the KPBL. Both measures were used as dependent variables in the model. The independent variables were the effect of free agency, amateur draft, the introduction of foreign players, a number of games in a regular season, and short-term shock due to an expansion of the league. The data consist of all regular seasons in the KPBL (1982-2016). The results of this styudy showed that only free agency and the number of games each team plays in a regular season were statistically significant in both SDWP and Gini models. The study found a significant decrease in standard deviation of winning percentages (SDWP) and Gini coefficient after the introduction of free agency in the KPBL. Also, competitive balance was increased as the number of games each team plays increase. However, this study did not found other structural changes to affect competitive balance in the KPBL. It may be due to the limited number of sample size based on the relatively short history of the KPBL(35 years). Since competitive balance is important for both the sport league and sport fans, baseball teams and the league should focus on maintaining and improving competitive balance in the KPBL.


The purpose of this study was to develop and validate a Rehabilitation Capability Questionnaire (RCQ) that could measure the rehabilitation capabilities of injured athletes. A total of 240 injured athletes engaged in physical rehabilitation programs in Study 1 which followed a method proposed by Cohen, Montague, Nathanson, and Swerdik (1988). Fifty-two injured athletes who had been taking a physical rehabilitation program participated in Study 2. The convergent, discriminant, and predictive validities of the RCQ were analyzed. The results indicated that the RCQ retained four factors 22 items: emotional, cognitive, behavioral, and social support factors. The RCQ showed good, external validity.

In this meta-analysis, we examined the relationships between two types of perfectionism (i.e., perfectionistic strivings and concerns) and athlete burnout. A total of 18 studies in 17 articles (i.e., one article included two studies with different data sets) were included and analyzed. Random-effects models were used to test the relationships between perfectionism and burnout in athletes. The results indicated that perfectionistic strivings were negatively related to athlete burnout while perfectionistic concerns were shown to be positively related to athlete burnout. Perfectionistic strivings are functionally adaptive to burnout in athletes, whereas perfectionistic concerns are functionally maladaptive to athlete burnout. Gender significantly moderated the relationship between perfectionistic concerns and athlete burnout.
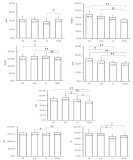
The relationships between bone properties and cumulative mechanical impact were examined in elite female athletes (N=70) and age, gender matched non-athlete controls (N=64). The athletes were divided into 3 groups, namely, high-impact (HI: body weight bearing with high mechanical loading, N=18), medium-impact (MI: body weight bearing with medium load, N=36), and low-impact (LI: body weight bearing with low load, N=16). Effects of mechanical impact on quantitative ultrasonography (QUS) parameters, including speed of sound (SOS), broadband ultrasound attenuation (BUA), and stiffness index (SI), were assessed using a multiple linear regression model adjusted for age, body weight, height, body mass index, and impact. We found that BUA was positively influenced by MI (P < 0.05). SOS was negatively influenced by LI (P < 0.05). SI was positively influenced by MI (P < 0.05). In conclusion, the bone qualities in elite female athletes differ depending on their cumulative impacts.
