ISSN : 1598-2939
ISSN : 1598-2939

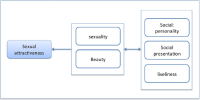
This study explains how women’s football strategically transfers the sports league’s image from hyper-sexualized women’s sports entertainment to the real football league. By focusing on the commercial messages from the Lingerie Football League and the Legends Football League, the author could understand the nature of the sexualized culture as the unique entertainment women’s sports league. By adopting reading sport critically (McDonald & Birrell, 1999), the purpose of this study is to understand the difference between the Lingerie and Legends Football League (LFL). This study further examined how women’s erotic capital performed in the LFL. Thus, in what follows, the author explores the extent to which the LFL strategically manages the mediated athletic bodies—in terms of adornments, types of movement, and media framing—presented to its viewership. In so doing, this analysis looks at the mediated feminine body as it is transformed, made into a site for maximum erotic capital. The findings indicate how the critical perspectives explain the LFL context and provide suggestions for further exploring a newly formed women’s professional sports league.


The objective of this study was to confirm the multidimensionality of varsity athletes’ commitment in NCAA Division I and Division II. A secondary purpose of this study was to examine the differences of commitment between Division I and Division II varsity student athletes. The instrument by Turner (2001) was revised in order to measure that commitment. The scale consisted of four bases of commitment including Affective Commitment (AC), Normative Commitment (NC), Continuance Commitment-High Sacrifice (CC-HiSac), and Continuance Commitment-Low Alternative (CC-LoAlt). A total of two hundred thirty five (235) varsity athletes in Division I and II participated in the survey. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was conducted to access the measurement model of athletes’ commitment and a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) was conducted to investigate the differences of commitment between Division I and Division II varsity student athletes. The CFA results indicated that the overall fit of the four bases measurement model was adequate. Overall, MANOVA was statistically significant. In a follow-up univariate test, there were significant differences in the “Affective,” “Normative” and CC:LoAlt” bases. Division I varsity athletes were more committed to “Affective” and “Normative” factors, while “CC:LoAlt” was a more important commitment for Division II varsity athletes.
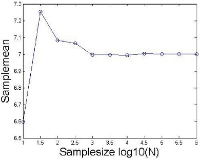
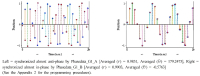
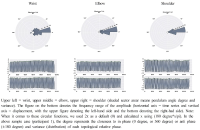
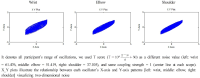
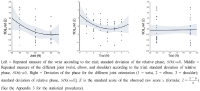
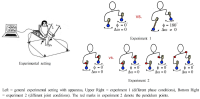
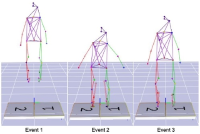
This study aims to represent a more preferential bilateral movement template by introducing empirical measures of cluster (Experiment 1) and fixed-point shift (Experiment 2) during the bimanual coordination. We showed how the phase dynamics can be calculated using the cluster method (analysis 1). Relatively stable patterns defined by the cluster process were employed for the fixed-point shift calculation to compare three joint oscillations (wrist, elbow, and shoulder; Analysis 2). The analysis revealed that (i) anti-phase coordination was less stable underlying the cluster phase and amplitude analysis; a significance that was mainly driven by higher radial variability. (ii) The three joint couplings and noise oscillations showed that they were wider for the distal (wrist) than the proximal (shoulder) areas. (iii) Repetition with one joint (i.e., wrist) may be significantly associated with trial effects; thus, using data of pick only one joint (wrist) but collecting data from different (three) joints seems more reliable to be a typical dependent variable for the trial effect. Observations and suggestions derived from this aspect represent how the bilateral movement calculation methods can be applied to measure the type of coordination stability eliminating of the learning effect stemming from numerous trials.

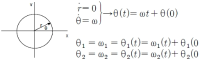
This cross-sectional study investigated the associations between health-related fitness and sleep quality and insomnia in 248 elderly women (≥65 years). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) and Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) were used to assess poor sleep quality and insomnia. Health-related fitness was assessed using a senior fitness test protocol. Subjects were classified in the high (high 33%), middle (middle 33%), and low fit (low 33%) groups based on the health-related fitness total Z-scores. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of poor sleep quality and insomnia according to health-related fitness levels. Compared to the high fit group (reference, OR=1), the low fit group had significantly higher OR for having poor sleep quality. Compared to the high fit group (reference, OR=1), the middle fit and low fit group had significantly higher OR for having insomnia. The findings suggest that higher health-related fitness via regular exercise and physical activity can help reduce the risk of poor sleep quality and insomnia in elderly women.
This study assessed the relative contribution of technical variables affecting birdies (Bir) and official money (OM) among the top 10 players of the Ladies Professional Golf Association. The average difference in performance variables was assessed according to prize money, country and continent, and time. Multiple regression analysis and one-way ANOVA were conducted, and a p-level less than .05 was considered statistically significant. First, putting average (PA) made the largest relative contribution to Bir and OM, followed by green in regulation (GIR). Second, players with highest prize-money earnings had significantly better drive distance (DD), drive accuracy (DA), sand saves (SS), and PA than median/lowest prize-money earners. Moreover, GIR was found to be accurate in distinguishing players’ prize-money rankings. Third, Korean and Oceanian golfers had significantly better PA than American and European golfers; Korean golfers demonstrated better Bir, Par3, Par4, and Par5 than players from other countries and continents. Lastly, women golfers’ performance improved in a 10-year-cycle. Particularly, DD, DA, and GIR significantly improved over each cycle, and Bir, Par3, Par4, and Par5, but not Eag, also significantly improved.
Although teams undertake various efforts (e.g., signing athletes who originate from the target market, holding international tours, participating in friendly tournaments during off-season) to expand their market internationally, teams signing target market’s national team level athletes is one of the most approachable and effective methods. However, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, no extant studies have empirically examined the effect of such a method. Therefore, the purpose of the current study was to examine the role of signing a national sports icon as a tool for market expansion for professional sports teams. This study conducted an experimental study by providing stimulus material and conducting a survey. The collected data was analyzed using the paired t-test and one-way ANOVA. Looking at the results, there was a significant difference in team loyalty when participants were exposed to the news that the team signed their national team player. In addition, the moderating effect of football involvement was evident as differences between the low involvement group and the high involvement group were partially statistically significant. Research findings contribute to understanding the effect of signing the target market’s athletes as a team’s global market expansion effort and provide important cues for future research.

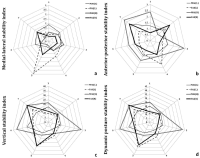
The purpose of this study was to investigate the analysis of the postural stability and leg stiffness according to the ankle instability types and bilateral legs during drop landing. Methods: Total 14 male athletes (n=7: mechanical ankle instability, n=7: functional ankle instability) Participants in the experiment. The leg stiffness, leg length, peak vertical force, loading rate, as well as the DPSI (medial-lateral [ML], anterior-posterior [AP], vertical [V], dynamic postural stability index) during drop landing were calculated. To analyze the variables measured in this study, SPSS version 21.0 was used to calculate the mean and standard deviation, while a two-way ANOVA was used to evaluate the ankle instability types (MAI, FAI) with landing leg (left: dominant, right: non-dominant leg) results. Dimensionless leg stiffness and change of leg lengths showed increased with significantly in non-dominant leg and MAI type than in dominant leg and FAI type. This resulted from decrease in the leg lengths with leg stiff. MLSI showed increased with significantly in dominant leg than in non-dominant leg during drop landing. Mechanically unstable individuals demonstrated increased leg stiffness, which may increase risk of musculoskeletal. Also, mechanically unstable participants demonstrated greater loading rate variability, which may indicate difficulty mitigating landing forces with lax ligaments.

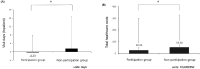
This study assessed the effects of participation in physical fitness assessment on healthcare costs by analyzing healthcare costs in those who did and did not participate in the physical fitness assessment for the National Fitness Award project conducted by the Korean government. The National Health Insurance Service database was used to compare healthcare costs in the years before and after participation in the National Fitness Award project for 318 individuals who participated (participation group) and 627 individuals who did not participate (non-participation group). Healthcare costs in the years before and after participation was different between the two groups. This difference was corrected for further analysis. Results revealed that the visit days (inpatient) was -0.23±8.16 and 1.53±8.16 days in the participation and non-participation groups, respectively, and was longer in the non-participation group. The change in the total healthcare costs was 28.56±272.88 ten-thousand KRW in the participation group and 53.36±275.33 ten-thousand KRW in the non-participation group, showing an annual difference of approximately 240,000 KRW in healthcare costs between the two groups. These findings suggest that participating in physical fitness assessments can have positive effects on participation in physical activities, thereby reducing healthcare costs.

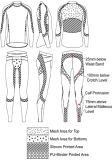
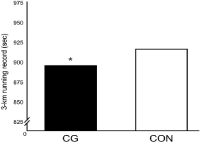
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of whole-body compression garments on aerobic and anaerobic performance, 3-km running record and physical fitness in amateur marathoners. Ten male amateur marathoners without any medical problems were measured compression garments following non-compression garments intervention (n=10, age: 25.40±2.72 yrs.; height: 173.71±3.52 cm; weight: 70.55±7.16 kg; body mass index: 23.34±1.70). The compression and non-compression garments intervention were conducted at weekly intervals. We measured aerobic and anaerobic performance, 3-km running record, and the physical fitness according to each intervention. As a result, VO2max, total exercise duration, anaerobic threshold were significantly higher in compression intervention than non-compression intervention. Also, minimum power was significantly higher in compression intervention than non-compression intervention. 3-km running performance was significantly faster in compression intervention than non-compression intervention. In addition, side-step was significantly faster in compression intervention than non-compression intervention. In conclusion, present study finding suggest that whole-body compression garments is beneficial to enhance aerobic performance and physical fitness.