A high percentage of young people have a sedentary lifestyle. However the young people with disabilities tend to be even less active. Schools are expected to play an important role in supporting an active lifestyle. It is crucial to better understand the determining factors which lead young people with disabilities to adopt active lifestyles. A study has been performed based on 15 case studies in different schools with a mixed method. Four principal categories of factors influencing an active lifestyle for young people with disabilities emerged from this study: adapted environment and universal accessibility, help and support, social interactions, and the quality of the experience. This study focuses on the measures to be put in place to support an inclusive experience in the field of sport and physical activity among young people with disabilities.
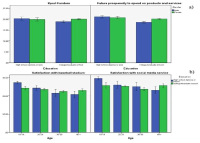
Despite the growing popularity of professional baseball in South Korea, academic literature lacks much quantitative analysis of its fans. The main purposes of this current study were two-fold. Firstly, it was to identify if fan attitudes and expenditures are associated with and different by demographic variables. Secondly, it was to find out if fan attitudes and expenditure positively predict and explain the variance of future propensity to spend on products and service. A total of 1612 fans who attended Korean baseball games voluntarily participated in this study. The survey questionnaire consists of five sections of demographics information, sport fandom, satisfaction of social media service, satisfaction of the baseball stadium, and future propensity to spend on products and service at the ballparks. An exploratory analysis found that fan attitudes and expenditures differed by demographic variables (e.g., gender, education, age). Second, fan attitudes about the baseball team, satisfaction with baseball stadium, satisfaction with team media social media services, and current venue expenditures proved to bepositive predictors of future propensity to spend on team products and service (FPSPS).

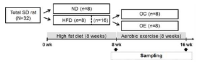
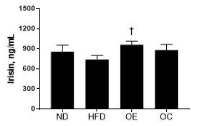
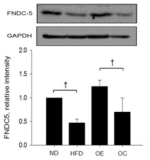
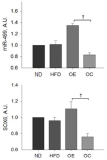
Obesity is known to be linked with a shift in skeletal muscle fiber type, which plays a role in insulin sensitivity and myokines activity. Here, we investigated whether aerobic exercise training has any effects on skeletal muscle MHC isoforms related to gene expression, irisin, and FNDC5 in obese rats. Thirty-two male SD-rats (3 wks old) were randomly assigned to normal diet (ND, n = 8) and high-fat diet (HFD, n = 24) groups, with specific caloric intake (ND; 11.5%, HFD; 60% of kcals from fat), for 8 weeks. After 8 weeks, HFD-induced obese rats were randomly reassigned to either an obese control (OC, n = 8) or obese exercise (OE, n = 8) group, and provided a normal diet. The OE group was exercised on the rodent treadmill (60 min, 15 m/min, 5 times) for 8 weeks. We investigated FNDC5, slow-twitch muscle gene (miR-499) and fast-twitch muscle gene (SOX6) expression in gastrocnemius muscle, and serum irisin. HFD group showed heavier body weight compared to ND group (p < .05). Blood glucose concentrations, determined by IGTT, were significantly higher in HFD group compared to ND group in 90-minutes and 120-minutes of the recovery phase (p < .05, 43%, 34%). Average body weight for the OE group was significantly lower than the OC group. The level of blood glucose in the OE group was lower than the OC group in 90-minutes and 120-minutes of the recovery phase (p < .05, 11%, 9%). Irisin levels were not significantly different between the HFD and ND groups. However, FNDC5 level was significantly lower in HFD rats than ND (p < .05, 53%). The OE group showed increased expression of irisin and FNDC5 compared to ND, but there was no change in OC (p < .05, 23%, 42%). While the levels of miR-499 and SOX6 were significantly higher in the OE compared to OC group, there was no change in MYH7. Taken together, 8 week regular aerobic exercise has positive effects on body weight, blood irisin concentration, its precursor FNDC5, as well as fiber type promoting genes mi-499 and SOX6.

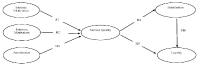
With the significant growth of the Korean baseball league for the past generation, sport managers and administrators in baseball are desperately looking for new revenue streams to bring more number of fans to the ballparks by offering value-added tangible and intangible products and services such as mascots, music, cheer-leadings, statistics, program books, and on-site promotion opportunities. In order to accomplish these set goals and objectives sport managers and administrators should fully understand who their fans are, what they want at the ballparks, and what makes them revisit the ballparks. The main purpose of this current study was to develop and validate fan motivation scale which is uniquely oriented to Korean baseball fans. A total of 1,927 surveys were collected and 1,869 were utilized in this study after excluding 58 surveys with incomplete or missing values. Reliability coefficients were calculated by factor and correlation coefficients were obtained by test-re-test reliability to remove inappropriate items. Confirmatory factor analysis was conducted to verify the structural model fit for the proposed seven-factor model after exploratory factor analysis through principal component with orthogonal rotation method. The newly developed seven-factor survey instrument consists of the fandom, regional connection, entertainment, dramatic curiosity, sense of belonging to the cheering team, ties with family members, and expertise.
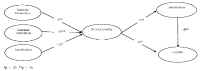
Competition among golf courses in South Korea for recruiting and retaining customers has increased dramatically over the years as the number of golf courses grew. Therefore, it has become important for golf course managers to understand what attracts golfers to their golf courses. The purpose of this study was to examine the relationships among motivation, service quality, customer satisfaction, and loyalty among recreational golfers in South Korea. Total 563 recreational golfers participated in this study and responded to a self-administered survey measuring the constructs. The result showed that intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation were positively associated with service quality whereas amotivation was negatively related to service quality. In addition, golfers’ perceived service quality had a positive impact on golfers’ satisfaction and loyalty towards golf courses. These results suggest that golf course managers should understand the types and levels of motivation golfers have and develop strategies for enhancing service quality.

Mental toughness (MT) is seen as an important psychological factor in the athletic success of elite athletes. Research on the subject has usually concerned male athletes. Our purpose was to investigate whether there are differences in mental toughness between female players who compete in an elite league and those who play at lower levels. In total, 298 female soccer players (M = 20.7 years, SD = 3.7 years) from three levels of Norwegian soccer responded to the Sports Mental Toughness Questionnaire. The MT Constancy subscale was removed from analysis due to an unacceptable Cronbach alpha (0.57). The results revealed that elite league players had significantly higher MT Global scores than those in lower leagues. The elite players had higher scores than the third league players on the MT Confidence subscale. For MT Control, the elite league players had a significantly higher score than the second league players, but the elite players did not differ significantly from the third league players on this subscale. These results partially confirm a relationship between mental toughness and playing level among female soccer players.
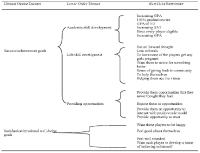
The purpose of this study was to identify effective strategies for life skill development utilized by coaches. Ten (10) veteran football coaches were recruited and interviewed. Each interview lasted approximately for two hours. All recorded data were transcribed verbatim and later used for further analyses. The results were presented in 13 parts organized by key interview foci: the role of academic coach; the typical day of academic coach; key components for program success; the goals of the academic coach; success stories; effective strategies; ineffective strategies; strengths of academic coaches; weaknesses of academic coaches; strengths of the program; limits of the program; gender/ethnic issues; and recommendations for future academic coaches. Positive youth development strategies were categorized into two hierarchical levels. One is global macro level strategies and the other is specific micro level ones. Based on the interviews, a number of youth development strategies, both in macro and micro level, perceived to be effective were identified. However, it should be noted that while the coaches perceived these strategies were effective, they were not viewed as a panacea for all athletes in all situations. Finally, based on findings from the current study, a model for effective life skills development strategies was proposed

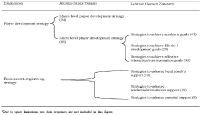

Osteoporosis is characterized by a loss of bone density and strength resulting in increased risk of fracture. One promising method for preventing fractures is participation in bone-strengthening physical activity. While the importance of mechanical loading for bone health is understood, assessment strategies are limited. Most researchers measure metabolic loads rather than mechanical loads, but not all activities that improve metabolic health increase bone strength. The osteogenic properties of physical activity (e.g., magnitude of the load, rate at which the load is applied, dynamic and odd nature of the load, duration of loading session, and breaks between sessions) have not traditionally been directly measured in health outcomes and surveillance research. The lack of research in this area has slowed our understanding of exactly what dose of bone-strengthening physical activity to recommend to the public as well as how to prescribe exercise to reduce the risk of fractures. To understand the influence of mechanical loading on bone adaptation, measurement methods must capture multiple physical activity dimensions (intensity, frequency, and time). Advancements in accelerometer technology now allow for the measurement of these dimensions. It is time that the lessons learned from using accelerometers in cardiometabolic health outcomes research be applied to musculoskeletal health.

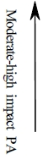
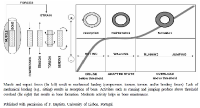
The purpose of this study was to test a protocol for establishing collective technical and tactical performance goals in elite men’s volleyball. The participants were a professional volleyball team. The period of study was one entire season. A baseline was established in the first half of the season, and the intervention was carried out in the second half of the season. The intervention involved the use of seven collective performance goals for monitoring the team in competitions. The variables studied were: the achievement of the collective performance goals that were established; the game phase; the result of the set; and the players’, coaches’, and psychologist’s perception of the use of the performance goals and the poster. The team slightly increased the number of goals achieved per game in the intervention period. There was a significant reduction in serve errors and a significant increase in block contacts. The intervention increased the players’ engagement with the team, although there were differences in opinion about the effect on the different players. The intervention improved the players' understanding of the match. The effects of the goal-setting and the poster were positively perceived, due to helping the players to understand their needs and the aspects to improve.

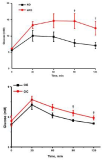
Purpose: To examine the concurrent validity of the T-REX accelerometer assessing physical activity against indirect calorimetry (oxygen uptake) and two different accelerometers (Actical and ActiGraph). Methods: Fifty healthy volunteers (25 men, age 23.5 ± 1.7 years; 25 women, age 22.4 ± 2.0 years) participated in tests using treadmill protocol. They walked or ran on a treadmill at four different speeds (4, 6, 8, and 10 km∙h⁻1 for men and 4, 6, 7.5, and 9 km∙h⁻1 for women) for 5 min at each speed. During the test, the T-REX (Taewoong Medical Co., Ltd., Korea) was attached at five locations on the body (ankle, arm, chest, waist, and wrist), the Actical was attached at two locations (waist and chest), and the ActiGraph was worn at the waist. Oxygen uptake (VO2) was measured using a portable device during exercise, and metabolic equivalents (METs) were calculated. The validity of the T-REX was assessed using Pearson correlations and Bland–Altman plots. Results: There were strong associations between T-REX and VO2 in men (r = 0.92–0.95) and women (r = 0.83–0.91) on the treadmill test (p<0.001). Associations between the T-REX and two different accelerometers (Actical and ActiGraph) were also strong (r = 0.89–0.98). Similar associations were also observed between VO2 and Actical (r = 0.87–0.95) and between VO2 and ActiGraph (r = 0.85–0.87). In the Bland–Altman plots, there were no statistical differences between VO2 and five T-REX sensor locations in both men and women (all p>0.05). Conclusion: The T-REX has a high concurrent validity with VO2 in assessing energy expenditure in men and women. This device might be an alternative to conventional accelerometers.
