 ISSN : 1598-2939
ISSN : 1598-2939
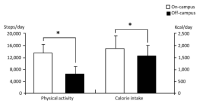
College freshmen usually face much stress and drastic environmental changes. These may influence health-related habits of college students. The purpose of this study was to compare and investigate the effect of residence on the levels of physical activity, diet patterns, and health-related habits between college freshmen who live on and off-campus. College freshmen (N = 71) participated in this study. Body weight, height, and body mass index (BMI) were measured. The level of physical activity was monitored and dietary patterns were analysed. Exercise, smoking, and drinking habits were surveyed. Physical activity was significantly higher for students living on-campus than for students living off-campus for both male and female. Calorie intake, monosaturated fat intake, and the frequency of alcoholic consumption were significantly higher for females living on-campus, while consumption of vitamins C and E were significantly lower for females living on-campus compared to their off-campus counterparts. We concluded that physical activity can be affected by where they live for both genders. Drinking habits and dietary patterns can be affected by their residence, especially for female students. Therefore, where college students live can be an important factor in impacting their health-related lifestyle

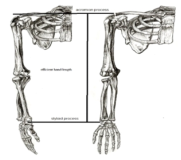
Purpose Recognizing the characteristics of elite athletes has a valuable significance in any sport for two reasons: 1) It leads to a high-level performance; and 2) this recognition helps us to determine the weaknesses and strengths of athletes. The present study was designed to compare the anthropometric characteristics, aerobic and anaerobic capacities of elite male Iranian fencers in three different categories (epee, foil and sabre). Materials and methods For this purpose, 24 fencers of Iran national senior fencing team were chosen and their anthropometric characteristics, somatotype, grip power, aerobic and anaerobic capacity of leg and hand, were measured. Results Statistical analyses of data showed significant differences (p<0.05) between lean body mass, weight and efficient hand length (EHL) of sabre and foil fencers. In addition, significant differences (p<0.05) were found between EHL and the difference between the length of two opened arms and height of epee and foil fencers. The amount of these variables were higher in epee than foil fencers. Aerobic capacities of epee and foil fencers were higher than sabre ones (p<0.05). The dominant somatotype for three categories was endomorphic mesomorph. Conclusion Based on the physiological and some anthropometric differences among the three fencing categories found in the present study, it could be concluded that the training programs and athlete selection criteria should be different among the fencing categories.

The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between measures of sprinting ability, fatigue index, lower body strength and power output, and aerobic fitness in well-trained, young, elite female soccer players. The descriptive cross-sectional design was applied to 30 well-trained female soccer players (mean ± SD: age 19 ± 4 years, body mass 57.5 ± 6.9 kg, height 167 ± 4 cm) who agreed to participate in the study. Tests of 40 m linear sprint, 7 x 30 m repeated sprint ability with 30 s recovery, sprint with change of direction, multi stage fitness test (MSFT), and vertical jump were conducted on a soccer field. The results showed that squat jump (SJ) had the strongest relationship with 0–20 m start and acceleration phases, while countermovement jump (CMJ) had the strongest relationship with maximal sprinting speed over 20–40 m. Aerobic fitness measures were significantly related to linear sprint over 0–40 m, 20–40 m sprint times, repeated sprint ability (RSA) fastest time, total time, mean time, and sprint with change of direction. Linear sprint over 40 m had a strong relationship with RSA fastest time, RSA mean time, and RSA total time. Finally, a significant relationship was observed between measures of linear sprint and sprint with change of direction. The relationship observed between aerobic capacity and sprinting abilities and the results from the stepwise analysis suggest that separate training strategies are necessary to specifically target and improve performance in these abilities.
The main objective of study 1 and 2 was to provide, within the framework of basic psychological need theory (BPNT), a mini-theory in self-determination theory (SDT), more in-depth understanding of the needs which athletes and coaches have in relation to each other. In particular, we wanted to investigate antecedents of the three basic psychological needs of athletes and coaches who compete at the elite level in sport. The two studies were conducted with the use of semi-structured interviews. Six former Norwegian world-class athletes participated in study 1 and four coaches with extensive experience within elite sport participated in study 2. In study 1, being seen as a whole person and being recognized in the planning process and the execution of athletes' training emerged as antecedents of autonomy. Help to improve skills and feeling supported as an athlete emerged as important for need satisfaction of competence and relatedness. Potential antecedents of need thwarting were also illuminated. In study 2, feedback on the quality of the coaches' work emerged as an antecedents of need satisfaction of competence. The need to know their athletes’ life situation and how they would think and feel in different competitive situations emerged as antecedents of the coaches’ need satisfaction of relatedness as it provided them with a sense of security. The results did not reveal any antecedents of need fulfillment of autonomy among the coaches. It was, however, revealed that athletes have the potential to thwart coaches’ needs. 241 words
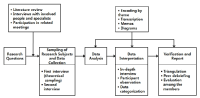
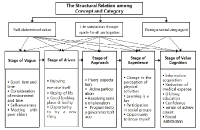
This study was for analyzing ethnographically the participation value of national-level sports-for-all programs perceived by the living-alone elderly. For this, specifically, we surveyed 16 living-alone elders aged over 65 among the participants of elderly sports-for-all programs provided by the National Council of Sport for All at 5 districts in Seoul, Gyeonggi, Incheon and made continuous comparison and analysis along the procedure of in-depth interview, data summarization, data arrangement, and conclusion drawing and verification. According to the results of analysis, a total of 38 concepts, 13 sub-categories, and 3 categories were derived, and the extracted three major categories were self-determined value, life satisfaction through participation in sports-for-all, and being a socializing agent. This study is expected to provide information recorded in the vivid language of elderly sports-for-all fields, useful in search for methodologies of research on the living-alone elderly, and valuable in making policies on exercise programs for the living-alone elderly.

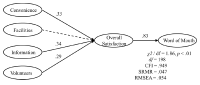
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among service quality, satisfaction, and the future intentions of users at the media center for Guangzhou Asian Games. A total of 295 users of media center from the 2010 Asian Games were invited to participate in a survey. A result of Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) indicated that all service quality attributes such as information, convenience, and volunteers had a positive effect on overall satisfaction excluding facilities. In addition, overall satisfaction had a significant effect on word-of-mouth (WOM). The findings of this study contributed to the field of sport media and event management by developing a better understanding of media center users at sporting event.
