The main aim of the present study was to investigate any effects from attention training techniques (ATT) on junior elite athletes’ perceived level of stress, perceived performance in sports, and perceived performances in school. Fifty-eight athletes from various sports such as alpine skiing, cross-country skiing, handball, biathlon, ski-jumping and Nordic combined completed an ATT training program over a period of 12 weeks. A pre-test/post-test control group design was used to investigate any effects from the ATT training program. The results from this study showed that there was a decreased level of perceived stress, and a positive change in perceived performances in sports, but not in school performances, among the athletes in the experiment group. There were no positive changes in the control group. The implications are discussed according to the changes in the athletes’ attentional awareness and control.
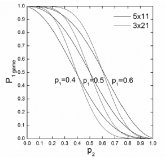
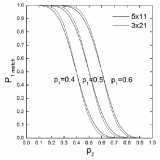
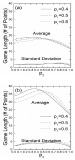
A model based on the probability of the server winning the rally was employed to evaluate the influence of the newly proposed scoring system, the best of five games of 11 points scoring system, being experimented by the Badminton World Federation on singles badminton matches. The model, based on the assumption of statistical independence on each point’s outcome, was used to generate predictions ranging from the game- and match-winning probabilities to game- and match-length statistics for matches under both the new and the current scoring system, the best of three games of 21 points. Validity of these results was checked against tournament data, four sets each for the two scoring systems, as well as previously published results, with satisfactory agreement in most cases. The results show that duration of singles matches would be reduced noticeably under the new scoring system without affecting the match outcome of the current scoring system.


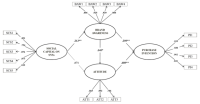
The aim of this study was to investigate how Generation Y consumers’ social capital on social network sites (SNSs) influences brand awareness and attitude towards purchase intentions for eco-friendly outdoor sportswear (EFOS). The result showed that social capital on SNSs has a positive effect on psychological perception of EFOS. Also, the perception of EFOS had not only a positive effect on attitude towards EFOS, but also directly affected purchase intention for EFOS. The outcomes of this study could offer sportswear marketers to understand Generation Y’s cognitive and behavioral involvement and to develop effective marketing strategies to promote EFOS. Therefore, Generation Y consumers’ purchase intentions can be fully stimulated.

This study analysed the influence of a 4 week combined weight bearing circuit exercise program in the body composition, physical fitness, and blood profile of an perimenopausal women (aged from 40 ~ 60, N = 29). Significant improvements were found in blood related parameters, fat-related parameters in body compositions and physical fitness parameters (P<0.01). As skeletal muscle mass (SMM) and lean % Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) considered as a standard for muscle mass in this study are used because each standard showed significant differences (P<0.01) and each standard significantly correlated with SMM, weight, time to exhaustion, fat-related parameters such as fa t% DXA, lean % DXA and free fatty acid in pre and post exercise. Blood-related parameters (creatinine, glucose, HDL-cholesterol, and total protein) significantly correlated with changes in each corresponding blood-related parameter after exercise (P=0.000). Exercise contributed to improving muscle mass-related parameters used as biomarkers in this study, which improved the positive changes of healthy indices are indispensable factors for evaluating the effects of exercise. These changes contribute to a virtuous cycle, which accelerates the capacity to perform exercise. It suggests that the weight-bearing circuit exercise can improve the quality of life of perimenopausal women.
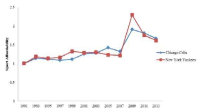
The cost of attending professional sporting events has been increasing steadily but the median household income has been relatively stagnant over the last three decades. While sport fans have increasingly spent more of their income on experiencing professional sport games, little information is available on a relationship between the costs of attending professional sporting events and sport consumers’ ability to pay and how this relationship has changed over time. Similar to housing affordability, this study proposed the concept of sport affordability, measured with a ratio between per capita income and the income needed to attend a sporting event and examined the degree of changes in the sport affordability index over time. The study results showed that the sport affordability index has become polarized among major league baseball teams. For 21 teams, the study showed that their sport affordability indexes have been deteriorating steadily over time but the trend was different for the other eight franchises. Policy and management implications related to equitable accessibility to sport and recreation events and marketing strategies are discussed.

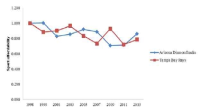
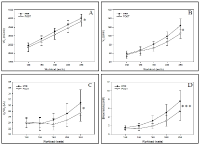
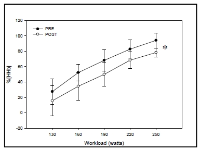
The purpose was to examine improvements of performance and different physiological parameters in ten trained male cross-country mountain bikers after a supra-maximal interval training (SMIT) program of 8 sessions. Each session comprised 60 to 90 repeated 1-minute bouts consisting of a 20-s effort at 115% of maximal aerobic power (MAP), followed by 40-s recovery at 50% of MAP. Performance time to complete the virtual time-trial performance test was reduced significantly by -4.2%. Pulmonary sub-maximal oxygen consumption and deoxyhemoglobin in vastus lateralis decreased significantly by ‑4.7% and -21.9% respectively during the MAP test. Our findings suggest that SMIT program might improve performance and cycling efficiency in XC mountain bikers.

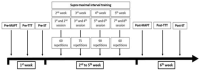
It has been suggested that highly motivated and passionate referees are more inclined to pursue higher league levels and, thereby, invest more hours in performance preparations and more general soccer activity. However, limited knowledge is available about practice and mental preparation among elite soccer referees. Our study aim was to investigate referees’ practice and involvement in unmediated soccer activity. We further sought to examine possible preparation differences between elite and sub-elite referees. Comparing elite with sub-elite referees practice may reveal underlying performance principles that may form a basis for trainings methods facilitating referee performance. The following hypotheses were tested: a) elite referees will report higher frequency of physical and mental training compared with sub-elite referees and b) elite referees will report higher involvement in unmediated relevant soccer activity compared with sub-elite referees. Among the 98 top-class referees in Norway, 83 (84.7% response rate, 73 men and ten women, aged 20–46 years) completed a survey about their training volume and content, mental training and involvement in unmediated soccer activity. Reported training volume and content are consistent with referees’ physical demands. Elite referees report significantly greater use of mental training compared with sub-elite referees, while there were no group differences on physical training volume and content or unmediated soccer activity. The results confirm only one of the hypotheses and support the assumption that mental training requires more motivation than physical training even though the latter has quantifiable results that are more regularly measured.
This study aimed to examine the degree to which service quality attributes can predict spectators’ revisit intention and word-of-mouth (WOM). A total of 551 spectators from a Formula One Chinese Grand Prix venue were selected to participate in a survey by using the convenience sampling method. Multiple regression analyses showed that service quality has a significant influence on behavioral intentions. Specifically, five of six service quality attributes (i.e., convenience, facilities, price, game experience, and promotion), had a significant effect on revisit intention, whereas four of six service quality attributes (i.e., convenience, facilities, game experience, and staff) had a significant effect on WOM. This study could suggest sport event marketers to consider functional services including price, location, and designation of the stadium or service place in order to attract more sport audiences.
Although many, likely most, athletes will not experience burnout in any meaningful degree in their sport endeavors, it can be an important concern for the psychological health and well-being of some athletes choosing to invest intensely in highly demanding competitive sport environments. This aversive chronic experiential state is of interest to clinicians and researchers alike because of its impact on athletes experiencing its characterizing symptoms. The phenomenon of burnout has been discussed and investigated in broader professional environments since the early 1970s (Freudenberg, 1974), but has only been a construct of interest among sport scientists, professionals and participants for about the last 25-30 years (see Smith, 1986; Dale & Weinberg, 1990 for early discussions of athlete burnout). After approximately a quarter century of examination, it is appropriate to take stock of the accumulated research on the athlete burnout construct at large. The purpose of the current review is threefold in nature. We start by remembering the important, groundbreaking athlete burnout research of the past but, guided by the prose of Walt Whitman, move on to outline potential future directions as “much unseen” remains relative to the understanding, conceptualization, and intervention/prevention of athlete burnout. Finally, we consider suggestions for how to unearth future burnout knowledge and/or implement the potential interventions outlined herein. So, while important conceptualizations and empirical studies in the area are reviewed, much of this information is delimited by reference to already available excellent reviews of athlete burnout research; although, some research immerging in the interim is also considered. Our goal is to take stock of the conceptual understanding and extant research on athlete burnout and to spark future research and practice as described herein by other researchers and clinicians. An endeavor of that sort inherently requires provision of some initial commentary on the construct and its development.
The purpose of this investigation was to examine the potential associations of motivational fluctuations during a full season with football players from one Premier Division team in Europe. Using correlational analyses we examined whether such motivational changes would mirror changes in stress perceptions (media and organizational) and performance anxiety levels. We used Achievement Goal Theory and Cognitive Activation Theory of Stress in the examination. In the elite sport setting, the endorsement of mastery involvement is recommended in order to avoid unnecessary stress and performance anxiety among athletes. 27 players (18-31 years old, Mage = 22.26 years, SD = 4.21) answered the questionnaires monthly over a season. We found that the athletes’ scores fluctuated over the season with interesting variations in the variables at time 2 (before season start) and time 7 (after the summer break) with a combination of high task orientation, high mastery climate perceptions and higher anxiety scores. The present findings revealed that stress may occur when there is a discrepancy between set values (what usually is) and actual value (what is). If the athletes are more accustomed to being evaluated normatively for the team roster, a sudden emphasis on personal improvement and maximum effort is very different – and may simply stress athletes even in a mastery environment.