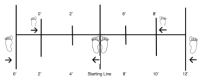
The ability to change directions, cut, and move quickly is paramount to success in basketball. Lateral shuffling movements or side-steps are common in basketball, but few tests incorporate these movements in measures of change-of-direction speed. Furthermore, no reliability or validity information has supported the most popular test, the Edgren Side-Step Test, and the procedures for the Edgren Test have been inconsistent. This study examined 4 lateral shuffle tests (LST), which combined different distances (8 feet and 12 feet) and durations (6 seconds and 10 seconds). All 4 conditions of the LST had very good internal consistency as the Cronbach’s α for each was above 0.889. All 4 conditions had very good test-retest reliability as the ICC (3,1) for each was above 0.930. None of the 4 conditions was found to have a significant relationship with a 20m sprint, whereas the 8x10-LST, r=-0.640, p = 0.046 and the 8x6-LST, r =-0.648, p = 0.043 had a moderate negative relationship with the Hexagon Agility Test. No condition was found to be a discriminator between recreational and competitive basketball players. Based on the results, the LST-8x6 and LST-8x10 appear to be valid and reliable tests for measuring change -of-direction speed.

The purpose of this study is to examine details of domestic and foreign papers that verified the effect of endurance training using molecular biological approaches and to investigate the directivity of molecular biological study, analytical technology and analytical factors for the analysis of training effects. Existing domestic and foreign papers on endurance training that investigated the effect of training based on molecular biological analysis of human beings were reviewed. In order to increase reliability of the selected papers and their compatibility with the purpose of this study, the papers were reclassified by a group of experts that consisted of physical education professors and doctors of exercise physiology. The final papers selected were studied for the change in hormones and enzymes through blood and muscular tissues based on study topic and trend analysis from a macroscopic perspective. Analytical methods used include western blot, RT-PCR, ELISA and immunohistochemistry of molecular biology. Analytical variables investigated / analyzed were ACE, ACTN, PPARs, UCP, mitochondrial DNA variant, creatine kinase, renin-angiotensin, AMPK for blood and COX, myosin binding protein C fast-type, glycogen phosphorylase, pyruvate kinase, GLUT, PPARs, and AMPK for muscle. Such molecular biological analytical techniques and variables should be widely used to provide 1) conditioning of professional athletes and life sports athletes, 2) analysis of training effect, and 3) scientific and future-oriented methods for health enhancement.
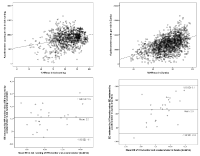
Most studies comparing objective measurements of physical activity are carried out on a treadmill or in free living activities and generally at low/moderate intensities. Purpose: To compare energy expenditure, correlation and exercise intensity measured by accelerometer and heart rate (HR) monitor during different exercises. Methods: This is a comparison study testing convergent validity between accelerometer and HR-monitor. A total of 26 participants (15 women) with a mean age of 21.8±2.4 years were included. The ActiGraph GT3X with 60 s epoch length was used to measure the participants’ accelerometer counts. HR was measured using Polar team 2 HR belts during 4x4 min running (four intervals lasting four minutes), 4x4 min spinning and Zumba. Results: Pearson correlation coefficient between mean % HR max and accelerometer counts was 0.69 in Zumba, 0.14 in 4x4 spinning and -0.42 in 4x4 running. Estimated energy expenditure from accelerometer was 2.25±1.69 kcal/min lower, i.e. 18.6 %, than energy expenditure estimated from HR monitor during 4x4 running. The corresponding numbers for 4x4 spinning and Zumba were 6.27±2.18 kcal/min lower, i.e. 55.7% and 2.64±1.78 kcal/min lower, i.e. 23.6%, respectively. A Bland-Altman plot shows that this difference increases with higher activity level in Zumba. For 4x4 min running the HR-monitor and accelerometer classified 76% and 60%, respectively, of the participants’ activity as vigorous intensity. Conclusion: A large instrumental variation in energy estimation across activities was found. Energy expenditure estimated by accelerometer was around 20% lower for 4x4 running and Zumba, and around 50% lower for 4x4 spinning, compared to energy expenditure estimated from HR monitor. The large variation in the correlation coefficients reflects the methodical differences explained in the paper.

The purpose of this study is to review how Korea Institute of Sport Science (KISS) had carried out sports talent identification and selection for enhancing athletic performance over the last three decades. In the 1980s, KISS had to prepare for the 1986 Asian Games and the 1988 Olympic Games. So, KISS developed test items for sports talent identification for various sports and had identified 4,359 sports talents over 30 sport events. Moreover, KISS developed the standards for elite athlete and had selected talented athletes using them. In the 1990s after the two big sports events, KISS established Talented Athlete Selection Center and constructed the foundation of elite athlete recruitment system. In the 2000s, Korea had suffered a lot of difficulties in recruiting new athletes because of government’s birth control policy effect and economic affluence. So, KISS developed an innovative sports talent identification program and had searched about 500 talented children every year. And KISS developed a new talented athlete selection program and had selected 1,682 talented athletes during 2000s. These new sports talent identification and selection programs are flourishing until now and would be the best sources of national team members in the future.
Culture has been studied as a factor that may account for physical activity disparities among different ethnicities in the U.S. Accordingly, acculturation has been one of the most prominent topics studied to explain mechanisms by which an individual or group may adopt a healthy or unhealthy lifestyle. Nevertheless, many studies lack the use of comprehensive theoretical frameworks, hence they are less informative for intervention design and implementation. This study was purposed to: 1) review important concepts of acculturation, and empirical findings regarding its association with physical activity participation, and 2) propose plausible syntheses of psychosocial theories of physical activity behavior and acculturative variables. The pros and cons of unidirectional and bidirectional models of acculturation were compared in terms of their theoretical plausibility as well as practicality. Acculturation has generally been found to be positively associated with leisure-time physical activity. Nevertheless, its impact on non leisure-time physical activity is still inconclusive. Lastly, we proposed that acculturation may affect physical activity participation through intrapersonal, interpersonal, and sociocultural streams of influence, adopting the typology of Flay et al.’s (2009) theory of triadic influence.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the specific computer programs used by sport organization personnel, the tasks they completed with those programs, and the expectations personnel possessed with regard to computer competencies they would expect from job applicants who hold a degree in sport management. Thirty-five practitioners employed at various sport organizations participated in semi-structured interviews. Participants utilized programs within Microsoft Office (e.g., Word, Excel) and Adobe Creative Suite (e.g., InDesign, Photoshop) to complete essential job tasks. Various specialty programs were also utilized. Job candidates were expected to possess familiarity and competence with programs used by the participants.
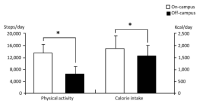
College freshmen usually face much stress and drastic environmental changes. These may influence health-related habits of college students. The purpose of this study was to compare and investigate the effect of residence on the levels of physical activity, diet patterns, and health-related habits between college freshmen who live on and off-campus. College freshmen (N = 71) participated in this study. Body weight, height, and body mass index (BMI) were measured. The level of physical activity was monitored and dietary patterns were analysed. Exercise, smoking, and drinking habits were surveyed. Physical activity was significantly higher for students living on-campus than for students living off-campus for both male and female. Calorie intake, monosaturated fat intake, and the frequency of alcoholic consumption were significantly higher for females living on-campus, while consumption of vitamins C and E were significantly lower for females living on-campus compared to their off-campus counterparts. We concluded that physical activity can be affected by where they live for both genders. Drinking habits and dietary patterns can be affected by their residence, especially for female students. Therefore, where college students live can be an important factor in impacting their health-related lifestyle

Purpose Recognizing the characteristics of elite athletes has a valuable significance in any sport for two reasons: 1) It leads to a high-level performance; and 2) this recognition helps us to determine the weaknesses and strengths of athletes. The present study was designed to compare the anthropometric characteristics, aerobic and anaerobic capacities of elite male Iranian fencers in three different categories (epee, foil and sabre). Materials and methods For this purpose, 24 fencers of Iran national senior fencing team were chosen and their anthropometric characteristics, somatotype, grip power, aerobic and anaerobic capacity of leg and hand, were measured. Results Statistical analyses of data showed significant differences (p<0.05) between lean body mass, weight and efficient hand length (EHL) of sabre and foil fencers. In addition, significant differences (p<0.05) were found between EHL and the difference between the length of two opened arms and height of epee and foil fencers. The amount of these variables were higher in epee than foil fencers. Aerobic capacities of epee and foil fencers were higher than sabre ones (p<0.05). The dominant somatotype for three categories was endomorphic mesomorph. Conclusion Based on the physiological and some anthropometric differences among the three fencing categories found in the present study, it could be concluded that the training programs and athlete selection criteria should be different among the fencing categories.

The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between measures of sprinting ability, fatigue index, lower body strength and power output, and aerobic fitness in well-trained, young, elite female soccer players. The descriptive cross-sectional design was applied to 30 well-trained female soccer players (mean ± SD: age 19 ± 4 years, body mass 57.5 ± 6.9 kg, height 167 ± 4 cm) who agreed to participate in the study. Tests of 40 m linear sprint, 7 x 30 m repeated sprint ability with 30 s recovery, sprint with change of direction, multi stage fitness test (MSFT), and vertical jump were conducted on a soccer field. The results showed that squat jump (SJ) had the strongest relationship with 0–20 m start and acceleration phases, while countermovement jump (CMJ) had the strongest relationship with maximal sprinting speed over 20–40 m. Aerobic fitness measures were significantly related to linear sprint over 0–40 m, 20–40 m sprint times, repeated sprint ability (RSA) fastest time, total time, mean time, and sprint with change of direction. Linear sprint over 40 m had a strong relationship with RSA fastest time, RSA mean time, and RSA total time. Finally, a significant relationship was observed between measures of linear sprint and sprint with change of direction. The relationship observed between aerobic capacity and sprinting abilities and the results from the stepwise analysis suggest that separate training strategies are necessary to specifically target and improve performance in these abilities.
The main objective of study 1 and 2 was to provide, within the framework of basic psychological need theory (BPNT), a mini-theory in self-determination theory (SDT), more in-depth understanding of the needs which athletes and coaches have in relation to each other. In particular, we wanted to investigate antecedents of the three basic psychological needs of athletes and coaches who compete at the elite level in sport. The two studies were conducted with the use of semi-structured interviews. Six former Norwegian world-class athletes participated in study 1 and four coaches with extensive experience within elite sport participated in study 2. In study 1, being seen as a whole person and being recognized in the planning process and the execution of athletes' training emerged as antecedents of autonomy. Help to improve skills and feeling supported as an athlete emerged as important for need satisfaction of competence and relatedness. Potential antecedents of need thwarting were also illuminated. In study 2, feedback on the quality of the coaches' work emerged as an antecedents of need satisfaction of competence. The need to know their athletes’ life situation and how they would think and feel in different competitive situations emerged as antecedents of the coaches’ need satisfaction of relatedness as it provided them with a sense of security. The results did not reveal any antecedents of need fulfillment of autonomy among the coaches. It was, however, revealed that athletes have the potential to thwart coaches’ needs. 241 words