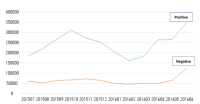
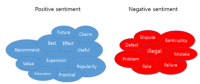
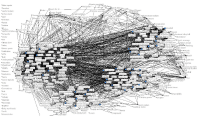
The purpose of the study was to explore public opinions and perceptions with regard to the Korean sport industry based on a big data analysis of social media content. Social big data was collected using ‘TextoM’, a big data analysis solution and ‘Naver’, an Internet portal service provider. In order to collect data, a total of 29 keywords were used such as sport industry, sport facilities, sport services, sport marketing, professional baseball, and sport manufacturing. Social analytics was used to analyze big data from social media content about the Korean sport industry. A total of 6,002,666 cases including document, web, blogs, and cafes (i.e., online community) with regards to the Korean sport industry were analyzed. Frequency analysis, keyword analysis through text-mining, sentiment analysis, semantic network analysis, and CONCOR network analysis were conducted. First, frequency analysis shows the volume of the Korean sport industry related searches stayed highly and increased. Second, keyword analysis through text mining was conducted to examine frequently used keywords in the sport industry. The analysis indicates four different categories of the Korean sport industry keywords such as sport games, sport goods, health, and sport policy. Third, sentiment analysis showed positive sentiment was found to have a greater weight than negative sentiment toward the sport industry. Fourth, semantic network analysis showed that the Korean sport industry connected with tourism, media, information, game, international, health, and culture. Last, the results of CONCOR analysis showed that the sport industry clearly divided into four different segments such as sport goods and equipment segment, sport facility segment, sport service segment, and professional sport segment. Results and findings are discussed and future research are suggested.


The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of a life skills-centered teacher professional development program on students’ perceptions of the learning climate and life skills transfer. Data were collected through a survey of 294 secondary school students (n = 183, experimental group; n = 111, control group) by administering the Learning Climate Questionnaire (LCQ) and the Korean Life Skill Transfer Survey (KLSTS) questionnaire. Data were analyzed using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 21.0. Results showed that there were significant differences in perceptions of the learning climate and life skills transfer between students in the experimental group and those in the control group (p < .05). Findings of the study indicated that a teacher professional development program can influence students’ perceptions of the learning climate, especially regarding autonomy, competence, and relatedness, thus promoting life skills development and transfer.
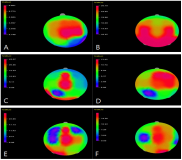
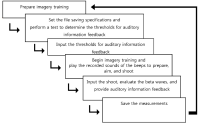
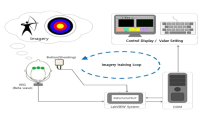
The present study aimed to test the effect of imagery training based on neurofeedback in elite archers of South Korea. Imagery training was provided to six elite archers, who imagined shooting three arrows in a set for a total of eight sessions. During imagery training, actual sounds recorded from an international archery Competition were played and Neurofeedback training was provided in a laboratory. In order to accurately measure EEG (Electroencephalogram), the archers were sufficiently rested, and the external environments were controlled before training began to prevent interference by artifacts. EEG was measured while the archers performed imagery training; real-time feedback was provided using vibrations when the waveform of beta waves was outside of the threshold determined for each archer. In addition, to test the effect of imagery training, scales assessing sports competitive state anxiety and sports imagery were administered before and after training, and pre-post changes were assessed. The results showed that in all archers, beta waves stabilized and vibration frequency decreased in post-measurement. Anxiety levels were reduced and imagery ability improved. Based on the findings, real-time neurofeedback training is believed to enhance athletes' self-regulation.

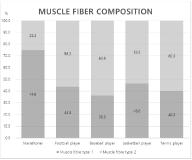
The objective of the present study was to assess muscle fibre composition by non-invasive methods for various sports events. 53 males of marathon (n=5), football (n=22), baseball (n=14), basketball (n=8) and tennis (n=4) athletes volunteered to participate in this study. The following 7 tests (overhead medicine ball throw, pull up, standing broad jump, sit up, shuttle run 10 x5, push up, vertical jump) are relatively easy to perform and to gather information about fibre composition through fitness levels. It can be used to assess the performance of strength using standard tables and to receive an indication of the degree of their share of fast (type II) and slow (type I) muscle fibres. For the study, a data analysis program in Microsoft Excel was used to view the mean and standard deviation of muscle fibre types. As a result, it was possible to speculate that the ratio of muscle fibre types differed according to the type of exercise. The results were obtained after sport motor tests of the mean value of muscle fibre composition by different sports events. Fibre type distribution remained with about 74.8% type 1 and 25.2% type 2 by marathoners, 43.8% type 1 and 53.2% type 2 by football athletes, 36.3% type 1 and 63.8% type 2 by baseball athletes, 46.6% type 1 and 53.5% type 2 by basketball athletes, and 40.0% type 1 and 60.0% type 2 by tennis athletes. Through these tests, the direction of the athletes’ muscle development can be considered, and it is possible to check the muscle fibre composition of elite athletes for the improvement of performance for each sport event. Moreover, it assumes that if this test is used for children, adolescents and young athletes, it will help to design scientific and effective training programs, thereby improving athletes’ ability to perform.

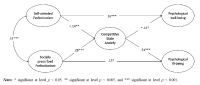
The study was to investigate the relationships between perfectionism (i.e., self-oriented and socially-prescribed perfectionism) and psychological well-being (i.e., vitality)/ill-being (i.e., emotional/physical exhaustion) and to examine the mediating effects of competitive state anxiety on the relationships. Three hundred two collegiate athletes participated in the study (Mage = 21.12yrs, SD = 1.28). The participants completed four questionnaires: Multidimensional Perfectionism Scale, Revised Competitive State Anxiety Inventory-2, Subjective Vitality Scale, and Emotional/Physical Exhaustion from Athlete Burnout Questionnaire. The hypothesized model presented an acceptable fit to the data. Specifically, χ2 (80) = 179.99 (p < 0.001), CFI = 0.973, TLI = 0.965, SRMR = 0.042, and RMSEA = 0.052 with 90% CI [0.042, 0.062]. The results indicated that self-oriented perfectionism was negatively related to competitive state anxiety (β = -.14, p < .005) and positively related to vitality (β =.26, p < .001), whereas socially-prescribed perfectionism was positively related to competitive state anxiety (β =.28, p < .001) and emotional/physical exhaustion (β =.15, p < .05). Competitive state anxiety was negatively related to vitality (β = -.14, p < .05) and positively related to emotional/physical exhaustion (β =.31, p < .001). Competitive state anxiety partially mediated the relationships between socially-prescribed perfectionism and emotional/physical exhaustion. The full mediating effects of anxiety on the relationships between self-oriented perfectionism and emotional/physical exhaustion and between socially-prescribed perfectionism and vitality were observed. Findings supported that self-oriented perfectionism was functionally adaptive to and socially-prescribed perfectionism was maladaptive to athletes’ psychological well-/ill-being.


The rules of modern pentathlon, in which the final ranking is determined by the results of swimming, fencing, riding, and laser-run, have been revised and managed by UIPM (International Modern Pentathlon Union). This study was conducted to evaluate the relationship between the score characteristics of five sports events and their influences on the final ranking, and to improve the UIPM's score conversion system, by analyzing the UIPM Level 1 final records of three years before and after 2017 when the swimming score system was revised. Independent t-tests revealed that laser-run performances improved significantly after the revision in 2017, while swimming performances got worse. The results of multiple regression analysis obtained through the four conversion scores showed that all four independent variables were significant. Considering the characteristics of Modern Pentathlon In Which The Importance Of Each Component Event Should Be Similar This Study Showed that the relative importance was biased towards fencing and the swimming event was neglected. Therefore, it seems necessary to change the swimming conversion score system to assess the players of modern pentathlon accurately and fairly.

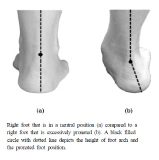
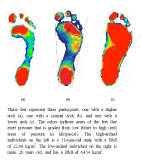
Foot arch structure contributes to walking in adults with obesity. However, little is known about the relationship between arch height and walking in these populations. The purpose of this study was to investigate if arch height affects gait characteristics among adults classified into three groups by body mass index (BMI). In this study, dynamic plantar pressure, spatiotemporal gait parameters, and lower-limb joint kinematics were collected from adults with normal weight (n=21), moderate obesity (n=18), and severe obesity (n=8) during walking at their preferred speed. Digital foot pressure data were used to compute a measure of arch height, the Chippaux-Smirak Index (CSI). Our results revealed that adults with higher BMI scores had lower arches than adults with lower BMI scores (p<0.01). Arch height was related to step width, double-limb support time, knee joint extension angle, and knee joint abduction angle (ps<0.01). Our results have implications for improving gait stability and increasing physical activity for obese populations via intervening in arch height.

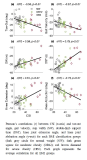
This study examines the relationship between player pay dispersion and team performance in the National Basketball Association (NBA) in North America. Specifically, the pay dispersion across teammates in each NBA team was analyzed according to four different models based on their playing time and team performance. Salary data for all NBA teams were collected over 23 consecutive seasons from between 1995-96 to 2017-18. Pay dispersion was measured using the Gini coefficient. Key findings are that the effects of the dispersion are positive for the model with all players in their teams, whereas the effects of pay dispersion on team performance are negative for the models with players who have more playing time, which indicates that greater pay dispersion among the most contributing players is associated with lower team performance. Teams should consider how they can more fairly allocate their capped payrolls among the highest contributing players on their teams based on the equity principle of distributive justice. Teams should consider how they prepare and incorporate other reward methods, such as signing bonuses, which may reduce injustice perceptions of underpaid players and eventually enhance team performance.
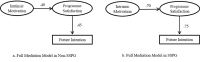
The Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology of the Republic of Korea introduced the ‘School Sport Club’ scheme to reinforce the extracurricular physical activities (PA) in schools. The effectiveness of the intervention was examined, and the results indicated that the students in SSPG schools had higher satisfaction with the programme and higher future intention to participate in the programme. Also, students’ future intention was found to be influenced by the indirect effect of intrinsic motivation which was mediated by their perceived satisfaction with the programme. Thus, it is important to provide a quality programme for promoting students’ participation in extracurricular PA programme.

The purpose of this study is to examine primary indicators for evaluating the defenders’ technical performance in football games. We collected a total 472 players’ match statistics of season 2017/2018 in tier 1 league of England, Spain and Germany and categorized them into central and wide. Principal component analyses are used to sort the indicators and using eigenvalues for an appropriate number of components. The results showed that “Tackles Lost”, “Defensive Errors” and “Errors Leading to Goal” were the primary indicators for central defenders and “Successful Take-on”, “Total Shots” and “Errors Leading to Goal” were crucial for wide defenders.