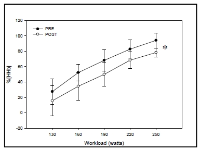
The purpose was to examine improvements of performance and different physiological parameters in ten trained male cross-country mountain bikers after a supra-maximal interval training (SMIT) program of 8 sessions. Each session comprised 60 to 90 repeated 1-minute bouts consisting of a 20-s effort at 115% of maximal aerobic power (MAP), followed by 40-s recovery at 50% of MAP. Performance time to complete the virtual time-trial performance test was reduced significantly by -4.2%. Pulmonary sub-maximal oxygen consumption and deoxyhemoglobin in vastus lateralis decreased significantly by ‑4.7% and -21.9% respectively during the MAP test. Our findings suggest that SMIT program might improve performance and cycling efficiency in XC mountain bikers.

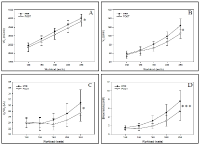
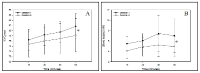
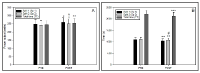
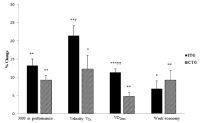
This study evaluates and compares the effect on endurance performance between high intensity interval training (ITG) and low intensity, longer-lasting training (CTG) with twice longer training time than ITG. We selected 22 healthy, non-smoking young men and women in a randomised trial to undertake either low intensity continuous training at 75% of maximal heart rate (HRmax) for 75 minutes or high intensity interval training at 90–95% HRmax, to undertake training either low intensity or high intensity three times a week for eight weeks. Performance times for running 3000 metres improved in both groups. Effect size between groups was 0.95 in favour of the ITG. Maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), running economy (RE) and speed at ventilatory threshold (VTh) improved in both groups. VO2max and speed at VTh improved significantly more in the ITG. RE did not differ between the groups. The result of this study indicate that high intensity training is more effective and time efficient in improving performance in recreational runners than low intensity continuous training.

This study was to examine the effect of competence on training engagement among shooting athletes. For this purpose, the data was collected from 102 participants with using Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI) and training engagement scale (TES). The data was analyzed by MANOVA, correlation analysis, and multidimensional analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, male athletes showed higher degree of cognitive and behavioral engagement than female athletes. In addition, the verification on differences in training engagement by career showed that athletes with 5 to 10 years of experience had higher degree of behavioral engagement than others. Finally, the analysis on verifying the relationship between training engagement and competence illustrated that competence was influenced by cognitive engagement. Therefore, cognitive engagement of athletes needs to be improved in order to increase the competence for shooting athletes.
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of reactive neuromuscular training (RNT) on golf swing kinematic sequence. RNT aims to develop effective dynamic stability or movement, minimize the need for verbal and visual instruction, and self-respond to stimulus created by outside force (eg. elastic band). A golf swing is a highly complex motor skill that requires multi-segments coordinative movement, such as golf kinematic sequence. To apply RNT to amateur golfers who tend to sway their body or head, inertial overloading technique utilizing clubbell (5kg) swing applied outside force (perturbation). Twenty-Four male amateur golfers were divided into two groups (RNT vs. Control). A golf ball tracking system (FlightScope Kudu) and 3D motion analysis system (K-vest) were selected for measurement devices. The experiment task was a 7-iron golf full swing. The carry distance, maximum angular velocity (pelvis, thorax, and wrist), and deceleration timing (pelvis, thorax, and wrist) were selected for dependent variables. The RNT group outperformed in carry distance. The maximum angular velocity of the pelvis and wrist were significantly higher in the RNT group. The deceleration timing of the pelvis and thorax significantly moved forward toward mid-downswing in the RNT group. The results of this study confirmed the motor learning effect of RNT on golf kinematic sequence and distance performance.
This single-case study explored the impact of eight sessions of psychological skills training to improve the performance of a student basketball player struggling with high negative emotions and underperforming due to limited psychological skills. The study participant underwent three baseline assessments of mood state, sports performance strategies (test of performance strategies), and perceived performance (perceived performance inventory and interview) before embarking on the A-B design intervention. Following the eight-week training program, consisting of 50–60 minute sessions encompassing MBTI/self-analysis, goal setting, relaxation/imagery training, self-talk training, concentration training, and routine training, assessments were repeated at four and eight weeks post-intervention. The quantitative data gathered from inventory scores were analyzed using Excel, and presented in a table. Qualitative data from interviews produced further insights into the patient’s experience. This study suggests that eight sessions of psychological skills training can effectively improve mood state, sports performance strategies, and perceived performance in student baseball players. This highlights the potential of such interventions to enhance athletic performance and well-being in individuals struggling with psychological barriers.
Environmental and maternal exercise experienced even during the very earliest stages of life has the potential to cause developmental changes. The growing evidence demonstrated that diverse environmental stressors affect offspring in various aspects in early stage of life and can be transmitted directly or indirectly by both parental lines. The development of normobaric hypoxic environment facilities began in recent years after athletes born and trained at high altitude continued to update their records in sports competition, especially marathons and other endurance sports. Although a large number of studies have proved the effect of hypoxic training in the field of sports science and competition, the effectiveness of this training model on exercise performance/capacity and physiological variables is still controversial. Therefore, this study makes a brief review of the papers related to this scope and attempted to understand the potential mechanism of maternal exercise in hypoxic environment on exercise performance and reduction of metabolic risk factors.
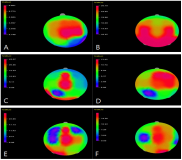
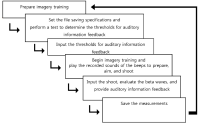
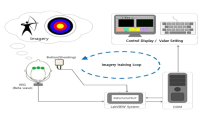
The present study aimed to test the effect of imagery training based on neurofeedback in elite archers of South Korea. Imagery training was provided to six elite archers, who imagined shooting three arrows in a set for a total of eight sessions. During imagery training, actual sounds recorded from an international archery Competition were played and Neurofeedback training was provided in a laboratory. In order to accurately measure EEG (Electroencephalogram), the archers were sufficiently rested, and the external environments were controlled before training began to prevent interference by artifacts. EEG was measured while the archers performed imagery training; real-time feedback was provided using vibrations when the waveform of beta waves was outside of the threshold determined for each archer. In addition, to test the effect of imagery training, scales assessing sports competitive state anxiety and sports imagery were administered before and after training, and pre-post changes were assessed. The results showed that in all archers, beta waves stabilized and vibration frequency decreased in post-measurement. Anxiety levels were reduced and imagery ability improved. Based on the findings, real-time neurofeedback training is believed to enhance athletes' self-regulation.

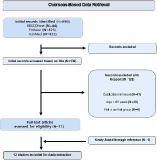
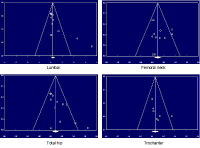
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between resistance training and bone mineral density of the elderly by using meta-analytic approach. A comprehensive literature review was conducted using such databases as EBSCOhost, Embase, and PubMed. A total of 12 articles were finally selected using the PRISMA procedure and analyzed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis (CMA) 2.0. The results were as follows. Resistance training had a significant positive relationship on bone mineral density in lumbar, total hip and femoral neck. However, resistance training did not have a significant relationship on bone mineral density in trochanter.

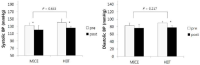
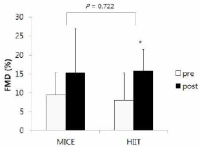
Background Several studies have recently shown that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) is superior to moderate-intensity continuous exercise (MICE) for improvements on endothelial in patients with cardiovascular disease. However, little is known about its effects on changes in blood pressure, especially in hypertensive patients. Purpose To compare the effects of HIIT and MICE on changes in blood pressure reduction and endothelial function in hypertensive patients. Methods Fourteen hypertensive patients, aged 52.1±7.6, participated in this study. They tapered off their medications, if necessary, and were randomized to either HIIT (n = 7) or CME (n = 7) group. HIIT was composed of 5 sets of 3 min exercise at 80% HRR, and each interval was separated by 3 min recovery at 40% HRR. MICE was composed of 35 min exercise at 60% HRR. Both groups were designed to use same energy expenditure, and performed exercise 5 days/week for 4 weeks. Endothelial function was determined by assessing endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) using flow cytometry and flow mediated dilation (FMD) using ultrasonography. Blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) were measured at rest by using automatic blood pressure monitor. Repeated ANOVA was performed to analyze if the changes in dependent variables after training are different between HITT and MICE group. Statistical significance was at p< .05. Results There was a significant interaction in resting HR, but not in BP, FMD, and EPCs between groups after training. Systolic BP was significantly decreased in both HITT group (p = .012) and MICE group (p = .048) after training. However, diastolic BP and FMD was significantly decreased (p = .021) and increased (p = .049) in only HIIT group, respectively. EPCs were not significantly changed after training in both HIIT and MICE group. Conclusion The results of this study indicate that there is no big difference in HIIT and MICE for BP reduction, and HIIT and MICE are both effective for BP reduction in hypertensive patients. However, further researches are needed to illuminate differential effects of HIIT and MICE on BP response and endothelial function.


The main aim of the present study was to investigate any effects from attention training techniques (ATT) on junior elite athletes’ perceived level of stress, perceived performance in sports, and perceived performances in school. Fifty-eight athletes from various sports such as alpine skiing, cross-country skiing, handball, biathlon, ski-jumping and Nordic combined completed an ATT training program over a period of 12 weeks. A pre-test/post-test control group design was used to investigate any effects from the ATT training program. The results from this study showed that there was a decreased level of perceived stress, and a positive change in perceived performances in sports, but not in school performances, among the athletes in the experiment group. There were no positive changes in the control group. The implications are discussed according to the changes in the athletes’ attentional awareness and control.