To date, research has rarely focused how a summer camp influences at-risk boys’ motivation and physical activity through a self-determination theory. This study examined changes of motivational and physical measures among at-risk boys participating in a summer sports camp. One hundred at-risk boys, aged 10-13 years, participated in a three week camp session. Two questionnaires and an endurance activity were completed by the boys as pre and post-tests. Results revealed amotivation increased and intrinsic regulation decreased across the camp session. Also, the boys’ endurance performance did not significantly change across the camp period. Findings suggest programs allowing more camper-centered choices and de-emphasizing competition may promote increased motivation and physical performance of at-risk boys.
This study investigates the effects from a 12-weeks mindfulness intervention on perceived stress, perceived performance in school and sports, and athlete burnout among junior elite athletes in sports. In the present investigation 50 Norwegian junior athletes from two different schools for elite sports participated in an experiment with a pre-test, post-test control group design. Twenty three of them were in the experiment group whereas 27 were in the control group. The athletes were from different sports such as cross country skiing, biathlon, shooting and track and field. As hypothesized, we found significant effects from the mindfulness intervention on athlete burnout. There were no significant effects found on perceived stress, perceived performance in school and sports. These findings are discussed in regard of applied implications and possible future research.
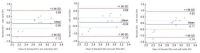
The purpose of this study is to verify the accuracy of energy consumption per wearing location (waist, wrist, ankle) of uniaxial accelerometer (GT1M) during horse-riding exercise (normal-walking, fast-walking, running). The study subjects were conveniently sampled from 11 males in their 20s from S horse-riding course who have over 3 years of experience in horse-riding and are licensed as leisure sports instructors (horse-riding), and the following conclusion was drawn. For normal-walking, there was no significant difference of standard energy consumption among waist, wrist, and ankle, and all three locations showed confidence interval with small deviation in Bland-Altman Plot. On the other hand, for fast-walking and running, only wrist showed no significant difference, where only wrist location showed low-deviation confidence interval in Bland-Altman Plot. According to such results, the accuracy was relatively high for wrist-wearing when predicting horse-riding activity energy consumption using accelerometer. Therefore, the wearing location must be considered when predicting horse-riding activity energy consumption with accelerometer on site.

The aims of this systematic review were to analyze the risks of renal injury during various sports and to recommend appropriate management with particular reference to individuals with a solitary kidney. The Ovid/Medline data-base was searched from 1996 to August 2015. The terms sports/sports medicine, athletes or physical activity were combined with the terms wounds and injuries/kidneys to yield 27 citations relevant to the review. This data base was supplemented extensively from journal reference lists and the author's personal files to provide a total of 56 citations. Review articles suggest that many physicians are still very cautious in recommending some forms of sport to children with single kidneys, while permitting other more dangerous activities. The absolute risks of renal injury are very low but not non-existent for most sports; for instance, there are 2.6 incidents per million exposures in male soccer players. Many renal injuries are minor, and only a small minority require nephrectomy. Contact sports account for perhaps a fifth of physical activity-related renal trauma, but the operation of all-terrain vehicles, cycling, Alpine sports and horse-back riding are all more common sources of injury. Possible factors modifying inherent risks include parental supervision, the wearing of protective equipment, initial renal health, and the individual's age (children being more vulnerable than adults). Minor renal injuries may require only 2-6 weeks of restricted activity; often, there are no long-term consequences, but subcapsular haematomas can cause a pressure necrosis of renal tissue, with later risks of hypertension, proteinuria and renal insufficiency. Sports physicians must communicate the objective level of risk to the parents of children with a single kidney, emphasizing that sport carries greater dangers for the head than the kidneys, and that serious renal injury is more likely from motor traffic than from sport participation. Moreover, they must underline the importance of continued regular physical activity to the overall health and development of the child. Nevertheless, they should also underline the need to take all reasonable precautions to reduce risk, including the avoidance of activities likely to involve collisions and blunt trauma.
The aim of this study was to investigate and analyze causes, times, regions, types, situations, first aid and treatment conditions of the injuries the boxing coaches. This study was conducted with a total of 80 subjects, who are currently active boxing coaches for middle school, high school, university, professional and national division. The tool used to investigate the nature of sports injuries of the boxing leaders based on the training environment was questionnaire, which is composed of 39 questions on age, sex, social background including leadership career, cause and time of injuries during training, type of region of injuries, injury regions based on type of training, first aid and treatment for injuries during training, and prevention of injuries. The questionnaire utilizes self-administered method. First, the form of training that exhibited highest injury rate during training was sparring, where attack type that most likely led to injuries was powerful hook. Second, the region of injury that exhibited highest injury rate during training was ligament injury, where upper limb area was more frequently observed than lower limb area. Third, most preferred emergency prevention method was ice packaging, and the most preferred hospital for treatment was western medicine based hospitals. Fourth, most of the coaches generally performed stretching before and after trainings. 16.25% of the coaches reported that they did not wear protection gears during training. In conclusion, this study that focused on causes, types, regions, first aid and treatment conditions of injuries for the coaches based on the training environment could aid in planning efficient measures for sports injuries of the boxing coaches and provide basic information to formulate treatment measures after injuries.
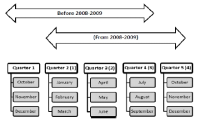
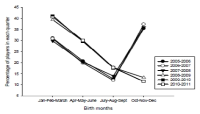
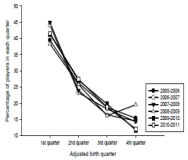
In most sports which are age-grouped annually, players born in the early part of a grouping period are more frequently found in subsequent categories over others from their cohort. This phenomenon is called the relative age effect (RAE). The goal of this research is to determine the impact of shifting the eligibility period on the RAE in elite minor ice hockey players in Québec. From 2002 to 2008, the reference date for allocating categories began October 1. In 2008, it was moved back to January 1. The RAE is reported for 6 seasons, 3 before and 3 after the reference cut-off date was moved back to January 1. Data from the 2005-2006 to 2010-2011 seasons were available for 13,982 minor ice hockey players. The RAE was present in each season before and after the reference date shift in 2008, as indicated by a significant over-representation of players from the 1st quarter of each competitive year whether it began October 1 or January 1. As an example, players born in the first trimester (October to December) of the eligibility year 2007-2008 represented 44.94 % of all Midget AAA players. After the shift, players from the first trimester (now January to March) of the 2010-2011 season were representing 41.57 % of all Midget AAA players and players from the fourth quarter (now October to December) were representing 12.16 %. Results confirmed the presence of a RAE in elite minor ice hockey whatever the beginning of the eligibility period. The RAE is a robust phenomenon and its impact is re-established rather rapidly when the cut-off date is changed.

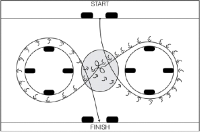
The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between specific off-ice variables and skating speed and agility among young ice hockey players. Fifteen male field players between ages 15 and 17 years took part in the study. Skating speed, agility test on ice, sprint, five-jump, squat jumps (SJ) and counter movement jump (CMJ) were included. Moderate to strong correlations were found between all the off-ice variables and skating speed. The strongest correlations were found between skating speed and 36 m sprint (r = 0.81, p < 0.01), and between skating speed and CMJ (r = -0.86, p < 0.01). There was no significant correlation between agility and speed skating, or between agility and sprint. Based on the results, there is reason to believe that an off-ice training program that includes sprint training and jumping exercises will have a positive effect on young hockey players’ skating performance.

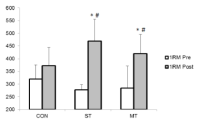
The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of traditional high volume multiple set resistance training and low volume progressive single set training on muscular strength and power in healthy male college students. A total of 19 students were randomly assigned to either a single set (ST, n=6), multiple sets (MT, n=7), or control group (CON, n=6). The ST (every 3rd day, 50-100% of 1RM, maximum 8 reps, single set) and MT (3 times/week, 70% of 1RM, 10 reps with 3 sets) trained for 8 weeks using an inclined leg press. One-repetition maximum (1RM), muscle maximal voluntary contraction, peak power, and electromyography were measured at baseline and after 8 weeks of training. Repeated-measured ANOVAs were used to find interaction effect between trial and treatment group factors. There was no significant increase on peak power after 8 weeks of resistance training both in MT (p = .286) or ST (p = .372). 1RM in both training groups was significantly increased compared to their baseline values (p < .001). However, there was no significant difference in 1RM between the two training groups after 8 weeks of training. It indicates that ST is as effective as traditional high volume multi sets training protocol (MT) for increasing muscle strength.

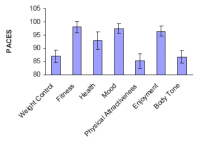
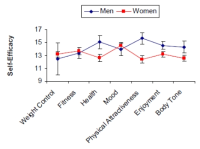
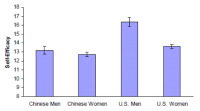
Background People exercise for different reasons. Reasons for exercise may influence exercise behavior via influencing important psychological factors of habitual exercisers, exercise enjoyment, and self-efficacy. The aim of this study was to explore how different reasons for exercise are associated with exercise enjoyment and self-efficacy by males and females from differing cultural backgrounds. Method Undergraduate students from a midwest university in the United States (males = 42, females = 171, age M = 21.68 years) and a national university in China (males = 64, and females = 149, age M = 21.47 years) participated in the study. Reasons for exercise, exercise enjoyment, and exercise self-efficacy were measured by questionnaire. Results Individuals who exercised for non-appearance based reasons reported higher levels of exercise enjoyment compared to students who exercised for appearance based reasons, and this finding was irrespective of cultural background or gender. Women who exercised for mood alteration reasons reported higher self-efficacy compared to women who exercised for other reasons. In addition, gender and cultural differences were related to reasons for exercise and self-efficacy. Conclusion Understanding exercise participants’ reasons for exercise and how these relate to their exercise enjoyment and self-efficacy may help to foster greater rates of physical activity participation.

This study was to examine the effect of competence on training engagement among shooting athletes. For this purpose, the data was collected from 102 participants with using Intrinsic Motivation Inventory (IMI) and training engagement scale (TES). The data was analyzed by MANOVA, correlation analysis, and multidimensional analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, male athletes showed higher degree of cognitive and behavioral engagement than female athletes. In addition, the verification on differences in training engagement by career showed that athletes with 5 to 10 years of experience had higher degree of behavioral engagement than others. Finally, the analysis on verifying the relationship between training engagement and competence illustrated that competence was influenced by cognitive engagement. Therefore, cognitive engagement of athletes needs to be improved in order to increase the competence for shooting athletes.