This qualitative study examined Korean college soccer players’ perceptions of and need for agents and the roles and competencies expected of them based on in-depth interviews with college soccer players. By exploring the significance of soccer agents as perceived by college soccer players, this study aimed to provide basic data necessary for training soccer agents for college soccer players and establishing regulations for college soccer agents. The research results can be summarized as follows: (1) The players interviewed generally showed a positive attitude toward soccer agents and were aware of the need for an agent; (2) the roles expected of an agent by college soccer players were different from those expected by professional soccer players: preparing opportunities to join Korean and foreign professional clubs, supporting and managing players, and facilitating smooth communication; and (3) the core competencies expected of a soccer agent by college soccer players were official agent certification, networks with professional soccer clubs, and understanding of the soccer industry. The results of this study highlight the need for stakeholder organizations in soccer to establish a systematic agent platform for college soccer players and take efforts to eliminate unregistered agents who engage in inappropriate activities. Qualified agent education and training for college soccer players will help protect them from unregistered agents and foster high-quality agency services.
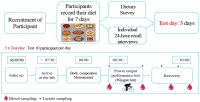
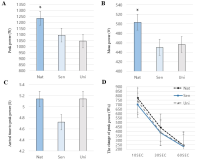
The aim of this study was to assess the eating habits of Korean wrestlers, and to explore the impact of differences in dietary intake on power output performance and blood lactate concentrations. Thirty adult wrestlers with more than seven years of experience each were included, grouped according to their competitive level (national, senior, and university team level). Participants recorded their dietary intake for seven days; nutritional analysis was performed using the CAN-Pro 4.0 software. After the nutritional survey, power output performance (Wingate test) was evaluated and blood parameters, including lactate concentration, were assessed. The wrestlers’ dietary assessments revealed differences in carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake among the groups, as well as differences in the peak power, mean power, and change in peak power, obtained from the Wingate test. Finally, the senior group had a significantly higher and lower lactate concentration than the university group immediately post training and 30 minutes post training, respectively. Follow-up studies should reveal more accurate associations between nutritional intake, nutritional quality, and performance. Finally, considering a study concerning nutrition and weight loss based on the results from this study, including not only wrestlers but also combat sport athletes will benefit nutrition education as well as athletes’ intake and performance.

This study aimed to describe and compare the pacing strategy and performance of world level under 19 (U19), under 23(U23) and senior single scullers during world championship races. Data are from 8 years of Rowing World Championships A and B finals of single scull races for U19, U23 and senior age scullers. Pacing was determined for velocity, stroke rate and, distance per stroke (SD). Scullers presented a fast start strategy for all races investigated. There was no significant difference in pacing between age groups. Velocity peaked at the 100m (U19) and 150m (U23 and senior) mark. The scullers in the older age groups showed superior performance scores of the studied variables. U19, Under 23 and senior single scullers present similar pacing regardless of their age group. Performance of single sculler improve from U19, to U23 to senior for both lightweight and heavyweight classes. The results of this study may serve as a reference for athletes, coaches, and sports scientists to be implemented in training.
The purpose of this study is to establish a simpler way to assess cardiopulmonary function in handball athletes whose continuous aerobic ability is vital in games using field tests, as well as to provide basic data on changes in lactic acid concentration. A total of 8 youth elite male handball athletes participated in this study. Participants visited three times in total. The first was assigned to graded exercise test and body composition measurements. Participants were then randomly assigned to a 20-meter shuttle ride or Yo-Yo Intermediate Recovery. All participants measured the lactic acid concentration after each exercise test. There were no significant differences in the VO2max (ml/kg/min) results in each test. There was no significant difference immediately after exercise of each test, after 5 minutes, after 10 minutes, and after 20 minutes. Compared to the golden standard GXT, there is no difference in maximum oxygen intake and lactic acid concentration after the two field tests, so both tests are expected to be efficiently used to evaluate the aerobic ability and develop training programs in the field.
The purpose of this study was to compare judo-related physical fitness, body composition, and isokinetic knee functions of male judo athletes from different age groups. Subjects for this study were thirty male judo athletes and randomly divided into three groups: cadet judo athletes (CJA, n=10), junior judo athletes (JJA, n=10) and senior judo athletes (SJA, n=10). Body composition, physical fitness, anaerobic wingate test, and isokinetic knee strength test were analyzed for comparing characteristics of judo athletes with age. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed Scheffe post hoc test. As the result of this study, body weight and muscle mass were significantly higher in the SJA group than those in the CJA group. The SJA group had significantly higher sit-up, vertical jump, side step and sit-and-reach values than the CJA and JJA groups, and the JJA group had significantly higher sit-up and back strength values than the CJA group. The absolute values of peak power (PP) and average power (AP) and relative values of PP in the SJA group showed significant differences compared to the CJA and JJA groups. Therefore, present findings provided research evidence that anaerobic power, maximal muscle strength and endurance would positively regulate performance of judo athletes with increasing age and athletic experience. Coaches and trainers in the field should try to provide a periodic training program to improve judo-related physical fitness and succeed.
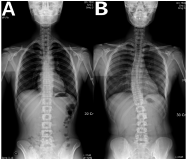
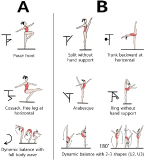
The study aimed to investigate the demographic and physical characteristics of South Korean female elite rhythmic gymnasts with scoliosis. Twenty-eight female elite rhythmic gymnasts aged 16.1 ±3.0 years were enrolled and divided by Cobb angle into a scoliosis group and a non-scoliosis group. In addition to the baseline characteristics of each group, visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for lumbago and results of the 36-item health survey version 2 (SF-36v2) questionnaires were collected. The pelvic tilt degree, leg length, hip range of motion and back-muscle strength were also measured and analyzed together. Radiographs of the thoracolumbar spine were taken for each subject. The scoliosis group (n=17) had significantly higher age, height, weight, and body fat compared to the non-scoliosis group. Further, six of the scoliosis group gymnasts had lumbar compression fractures or spondylolysis. Spinal flexors and extensors of all the subjects were balanced in strength but the lateral flexors showed noticeable imbalance. Elite rhythmic gymnasts were found to be increasingly susceptible to scoliosis and other spinal disorders with age and years of training. Spinal lateral-flexor muscle imbalance was more severe with scoliosis.


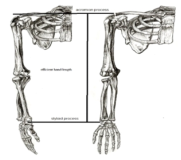
Knee joint valgus is often implicated as a hazardous position for the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and has been linked to ACL injury risk. Although several groups have previously examined racially diverse cohorts to determine if there are predispositions for injury, there is little evidence found that explore sex differences in valgus angles in African American athletes. The purpose of this study was to identify the difference of the knee valgus angles between African American male (AAM) and female (AAF) student-athletes. Eighty-five National Collegiate Athletic Association, Division II African American male (n=36) and female (n=49) student-athletes participated in this study. Subjects dropped directly down off a box and immediately performed a maximum vertical jump. Valgus and flexion angles were analyzed and calculated based on the relationship of the tangent for each image. Knee valgus angles were significantly different between AAM and AAF athletes both at initial contact and maximum valgus displacement (p<.05). Significant differences in knee flexion angle was observed with the AAM having greater Initial Contact knee flexion (p<.05). The current data indicates that sex differences, specifically increased knee valgus angles, exist during jumping and landing. Neuromuscular training programs should be designed to specifically address excessive valgus knee motion and improve landing knee flexion among these athletes.


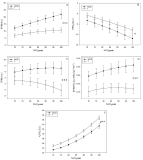
This study aimed to compare deoxygenation in the vastus lateralis in the skeletal muscle microvasculature of nine world-class/elite (WC/E) vs. thirty-one well-trained/trained (T) cyclists by near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) during a maximal aerobic power (MAP) test. Interaction analysis showed that 1st degree polynomial trends across % peak oxygen consumption (%VO2peak) differed significantly between WC/E and T cyclists on deoxygenated hemoglobin-myoglobin (Δ[HHb]) and on total hemoglobin-myoglobin (Δ[THb]) from 70 to 100% of VO2peak. These results show that the linear slopes of these trends were different. Near-plateau of Δ[HHb] was observed in T cyclists, whereas a consistent increase up to VO2peak was seen in WC/E cyclists. The Δ[THb] curve declined in T cyclists suggesting that blood volume in the vastus lateralis microcirculation decreases from 70 to 100% of VO2peak whereas it increases slowly but continuously to 95% of VO2peak in WC/E cyclists. The results of this study showed that deoxygenation in the vastus lateralis increases consistently up to VO2peak in WC/E cyclists and seems to be influenced by blood volume in the microcirculation.

The main objective of study 1 and 2 was to provide, within the framework of basic psychological need theory (BPNT), a mini-theory in self-determination theory (SDT), more in-depth understanding of the needs which athletes and coaches have in relation to each other. In particular, we wanted to investigate antecedents of the three basic psychological needs of athletes and coaches who compete at the elite level in sport. The two studies were conducted with the use of semi-structured interviews. Six former Norwegian world-class athletes participated in study 1 and four coaches with extensive experience within elite sport participated in study 2. In study 1, being seen as a whole person and being recognized in the planning process and the execution of athletes' training emerged as antecedents of autonomy. Help to improve skills and feeling supported as an athlete emerged as important for need satisfaction of competence and relatedness. Potential antecedents of need thwarting were also illuminated. In study 2, feedback on the quality of the coaches' work emerged as an antecedents of need satisfaction of competence. The need to know their athletes’ life situation and how they would think and feel in different competitive situations emerged as antecedents of the coaches’ need satisfaction of relatedness as it provided them with a sense of security. The results did not reveal any antecedents of need fulfillment of autonomy among the coaches. It was, however, revealed that athletes have the potential to thwart coaches’ needs. 241 words
Purpose Recognizing the characteristics of elite athletes has a valuable significance in any sport for two reasons: 1) It leads to a high-level performance; and 2) this recognition helps us to determine the weaknesses and strengths of athletes. The present study was designed to compare the anthropometric characteristics, aerobic and anaerobic capacities of elite male Iranian fencers in three different categories (epee, foil and sabre). Materials and methods For this purpose, 24 fencers of Iran national senior fencing team were chosen and their anthropometric characteristics, somatotype, grip power, aerobic and anaerobic capacity of leg and hand, were measured. Results Statistical analyses of data showed significant differences (p<0.05) between lean body mass, weight and efficient hand length (EHL) of sabre and foil fencers. In addition, significant differences (p<0.05) were found between EHL and the difference between the length of two opened arms and height of epee and foil fencers. The amount of these variables were higher in epee than foil fencers. Aerobic capacities of epee and foil fencers were higher than sabre ones (p<0.05). The dominant somatotype for three categories was endomorphic mesomorph. Conclusion Based on the physiological and some anthropometric differences among the three fencing categories found in the present study, it could be concluded that the training programs and athlete selection criteria should be different among the fencing categories.