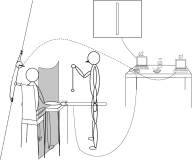
The current study attempted to develop a web-based state aggression measurement program (WTCRTT) and examine its applicability in terms of validity and reliability by conducting laboratory experiments. A repeated experimental design was employed, where subjects were exposed to both violent and non-violent media content. A physiological measure was also included to test the internal validity of media stimulation. The results showed the WTCRTT is a valid measure of behavioral aggression as the hypotheses on construct validity and internal validity were supported. For instance, the WTRCTT after exposure to violent media was positively correlated to anger, physical aggression, and total trait aggression scores. The WCRTT that was developed and tested in this study can be used not only by the scholars interested in aggression research with no cost and but also by the parents who want to monitor their children’s state (i.e., behavioral) aggression.
The purpose of this study was to explore the meaning of the coach-athlete relationship for two Norwegian male super-elite athletes. By means of semi-structured interviews and the use of Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis (IPA) the results revealed four emergent themes that represent underlying dynamics that influenced the athletes’ perception of what constitute an effective coach-athlete relationship; 1) Extreme independence. 2) Coaching without skills? 3) The coach as a butler, and 4) Expectations – make it or break it. These underlying dynamics are further discussed using the theoretical frameworks of coping strategies and power with the need for control as an important common denominator.
The aim of this study was to develop consensus of opinion from expert netball coaches by exploring prime defining characteristics of, and prime development requirements for, coaching expertise. Forty-eight expert female netball coaches representing five domains were recruited. A four-round Delphi Poll technique was utilised to generate consensus of prime characteristics of expertise and prime development requirements. Distinct characteristics of expertise were identified in each domain. The domain-specific characteristics of expertise dispute the appropriateness of a one-size-fits-all coach development approach such as coaching courses which are not bespoke. Concerning development requirements, the findings demonstrated support for individualised, predominantly informal approaches.
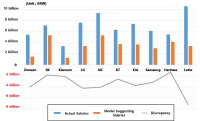
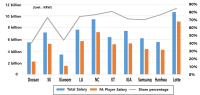
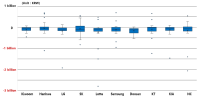
The purpose of this study is three-fold. Firstly, it revisits and updates the prevailing model (Park et al., 2018), by adding players’ field performance data from the past three seasons (2017 to 2019). Secondly, it verifies the effectiveness of the modified salary calculation model by comparing the top 20 ranked players’ actual salaries with model Expected Monetary Value (EMV). Lastly, it elaborates and refines the model to enhance its applicability for the Korean market. The results indicate that all 10 Korea Baseball Organization (KBO) teams paid players much more than what was required. Also, according to the proposed salary calculation model, SK Wyverns was the most efficient team (i.e., smallest difference between total team salary and EMV) while Lotte Giants was the least efficient. Finally, expert panels suggest that the salary calculation model be used as a supplementary tool because the model does not count such factors as defensive position, leadership, contribution to winning, physical conditions, past injuries, and defensive skills.

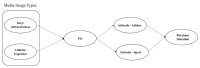
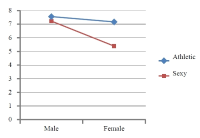
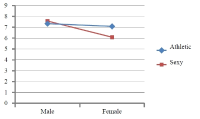
This study was to examine how different media images of female athletes’ impact women’s sports ticket sales for women’s sports spectatorship. This study interested in exploring the mechanism of buying a ticket for women’s sports event. The authors further analyzed what mechanism of women’s spectators’ intrigue to purchase the ticket for women’s sports event. As a theoretical framework, this study based on match-up hypothesis and associated learning theory to investigate spectators’ perceptions about female athletes’ presented media images on promoting their sport event ticket; this study explored (a) Fit: perceived appropriateness of the endorser (female athlete) with image type (athletic or sexy), and (b) Attitudes: how to fit impact on spectators’ attitude toward athlete and attitude toward sport separately, and (c) purchase intention to sport event. By adopting a 2×2 experiment design study, participants’ gender and image types manipulated. The participants (n = 113) were randomly assigned one of four conditions. The results indicated that the interaction between participants’ gender and image types was significant. Also, there was gender gap on women’s sports spectatorship in fit and attitude toward female athlete and women’s sport, and purchase intention to the sport event. The finding showed that male participants’ attitudes toward the athlete decreased more in response to the athletic image than the sexy image. Males preferred to see the sexy image while women do not want to see this type of image. Sports marketers need to know this perspective to sell their products and sporting event tickets. Thus, this study conclude that sex sells marketing does not promote women’s sports for either gender.



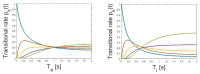
This study measured haptic extra accuracy, that is, judging one hit position in a hand-held object. Primarily, which factors are associated with the estimation of the contact position when an impact is made on the grasped implement. Data were collected from 20 participants and their extended haptic accuracy were analyzed using a discrete numerical state, as well as the stochastic evolutionary possibility. Analyzations proved that perceived accuracy influenced not only the stimulus magnitudes distinguished by the coefficient of restitution, but also the distributions of the encoded impressions by the rotational inertia. In particular, stochastic analysis confirmed that perceiving the location of the effect of grasped objects is more constrained by kinesthetic oriented property than by the cutaneous oriented gain in arbitrarily conflicted circumstances. The results from the analyzations suggest a broader hypothesis for further research into the effects of inertia tensor related to haptic spatial accuracy in a hand-held object.

The purpose of this study is to present retirement age predictive functions of athletes that can be utilized as data to reduce psychological shock of athletes from retirement and prepare for the future. To accomplish such purpose, athletes who retired as an undergraduate, unemployed or professional registered on the athlete registration system of the Korean Sport & Olympic Committee for three years were selected as the population. Stratified sampling was used for convenience sampling. Content validity of a retirement factor questionnaire was examined by consulting with experts. Opinions of 72 retirees were collected through an open questionnaire, and samples of 260 persons were used in the first and second parts after consulting with experts based on first sample data. The stepwise regression analysis method was applied to develop reliable and valid retirement predictive regression function. The degree of relevance was shown by multiple correlation coefficient between predicted age calculated by the predictive function and actual retirement age. Significance level was .05 for all tests. The 8 predictive function are presented according to the procedure above. Y^1(retirement age of female athlete)= 24.097+1.778*(physical limitation 11)-1.142*(job plan29), Y^2(retirement age of male athlete)= 23.498+1.334*(popularity 2)-1.126*(exercise attitude 20)+1.021*(competitiveness 7)-1.020* (job plan 29)+0.871*(economy 18)-1.905*(administration 22)-1.024*(administration 23)+.778*(interpersonal relationship 13), Y^3(retirement age of combat sports)=23.158+.688*(physical limitation 11)-1.790*(job plan 29)+0.960*(popularity 1)-0.656*(exercise attitude 16)+0.747*(job plan 33)+0.643*(economy 18)-0.461*(administration 23)+.606*(injury 46), Y^4(retirement age of non-combat sports)=20.741+ 1.637*(popularity 2)-1.270*(exercise attitude 20)+0.942*(competitiveness 7)+2.061*(family 5)-3.291*(administration 21)+1.082*(administration 25)+1.192(interpersonal relationship 8), Y^5(retirement age of individual sports)=27.414-1.295*(job plan 29)+1.463*(physical limitation 15)+0.972*(popularity 1)-0.639* (exercise 16), Y^6(retirement age of group sports)= 21.950+1.950*(popularity 2)-1.318*(exercise attitude 20)+4.635*(interpersonal relationship 6)-3.337*(addiction 41), Y^7(retirement age of undergraduate athlete)= 21.950+1.950*(popularity 2)-1.318*(exercise attitude 20)+4.635*(interpersonal relationship 6) -3.337*(addiction 41), Y^8(retirement age of unemployed and professional athlete)= 27.808-0.874* (exercise attitude 19)+1.287*(competitiveness 8)-1.402*(administration 21)+0.757*(popularity 2).
This study aimed at testing a theoretical framework applicable to equestrian participation process based on revise PCM. This study revisited and revised PCM to deal with limitations that an initial model has, and analyzed the framework in terms of equestrian activity to understand equestrian participation process as a whole. The study model was tested among equestrian participants in Korea and used survey method to collect 320 questionnaires. Total 312 questionnaires were analyzed by SPSS and AMOS, and used to conduct frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. The results are as follows. First, favor on a horse and achievement factors positively affected all the involvement factors, and media and promoting friendship factors positively affected self-expression and centrality factors. However, pursuit of health factor did not affect all the involvement factors. Second, attraction factor had positive effect on volitional choice factor however no effect was observed on informational complexity or position involvement factors. In addition, centrality factor did not affect all the commitment formative factors while self-expression factor positively affected all. Third, informational complexity and volitional choice factors had positive effect on resistance to change factor, however, position involvement had no effect on resistance to change factor. Fourth, resistance to change factor positively affected loyalty factor.

Homeless World Cup (HWC) program contributes to supporting and inspiring homeless people in order to positively change their own lives. There has been diverse research on the HWC, but most have emphasized outcomes. An effort for understanding of specific motivation process still remains scarce. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to understand the motivational process of the participants and describe the process in view of ERG theory. For the study, qualitative approach is conducted with using semi-structured interview. Findings show that the motivation could be thought as a result of their feeling of security, self-esteem and the desire to achieve their goals. Their behavioral changes toward others are related with the satisfied their psychological basic needs, and existence needs seemed to be based on the social relationship. In spite of several limitations, the findings give a chance to consider about how the HWC program should be developed.

In this article, I develop a scale for measuring social capital scale in a sports club (SCSSC) to review the concept of social capital based on sports club members and construct social capital scale in a sports club context. This article employees the methodology of scale development, which involves three studies: Study 1, qualitative assessment for scale generation was insisted with an in-depth interview and focus group interview. To address scale development, two times quantitative surveys were conducted. Study 2, for scale refinement, used parallel analysis and exploratory factor analysis. Study 3, confirmatory factor analysis to confirm the essence of the SCSSC construct and its' dimensionality. In order to verify the hierarchical properties of the factor structure, higher-order factor analysis was implemented by dividing the above factors into a single factor and double factors. After comparing the two types of factors, results reflected a hierarchical relationship between the single factor and 5 sub-factors of social capital in sports clubs. Lastly, in order to verify the predictability of the deduced scale, satisfaction of life was used as a dependent variable to conduct a causality analysis in which results showed a statistical signification relationship.