The purpose of this study was to examine the mediating effect of emotion regulation in the relationship between perfectionism and self-handicapping. After 503 college dancers (414 females, 89 males) completed the battery of questionnaires, the data were analyzed for descriptive statistics and analyzed by frequency analysis, correlation analysis. The bootstrapping method was used to verify the statistical significance of the indirect effect. The results showed that the reappraisal of emotion-regulation significantly mediated the relationship between self-oriented perfectionism and behavioral self-handicapping. Also determined that the suppression of emotion regulation significantly mediated the relationship between socially prescribed perfectionism and claimed self-handicapping. This study demonstrates that perfectionism and self-handicapping will have a different relationship depending on dancers’ types of emotion regulation. These findings provide valuable information on the psychological coping strategies used to control the negative emotion that are related to perfectionism among dancers.
Previous research points out high relevance of maximal strength measurement in the diagnostics of different populations. However, there is inconsistency in procedures of maximum strength measurements. Thus, it must be questioned whether the results from different studies are actually comparable. Due to the aforementioned problems in standardization, the aim of this study was to assess correlations between and reproducibility of isometric and dynamic strength testing. Since there are many studies investigating maximal strength in the calf muscles, this study will examine the plantar flexors. For this purpose, 87 active participants were recruited (m: 52, f: 35, age: 28.3 ± 5.5 years, range 18–38 years, height: 178.3 ± 6.6 cm, weight: 81.5 ± 7.4 kg) who performed maximal isometric strength testing and dynamic 1RM testing in plantar flexion both with extended and bended knee joint. Pearson correlation as well as concordance correlation coefficient (CCC) were determined. In literature, CCC is used to determine reproducibility between two different testing methods. There were correlation coefficients of r = 0.63 – 0.77 and ρC=0.62 – 0.77. Results are comparable with correlations between maximal isometric strength and 1-RM in previous studies in different movements. In consideration of CCC, isometric strength testing and 1RM seem to not measure the same parameter, therefore comparison of results measured with different procedures seems difficult. Our results exhibit a high influence of isometric maximal strength on 1RM performance. However, 1RM tests cannot be replaced by isometric strength testing. Care must be taken due to standardization of procedure when comparing results from different studies and, especially, if 1RM testing should be replaced with isometric strength measurement.
This experiment is designed for bone health in wrestlers and martial arts athletes who lose weight with Rapid Weight Loss (RWL). To clarify the effect of iron intake on the relationship between weight loss and bone densityFor athletes using the RWL strategy, iron intake was observed for bone mineral density (BMD), serum osteocalcin (OC) level, and serum iron marker. This study was conducted on 23 wrestlers (13 males and 10 females). It was divided into the trial 1 (iron intake and weight loss) and the trial 2 (only weight loss). In addition, between the first and second experiments, a washout period was given for 3 weeks} in order to eliminate the medicinal effect. All measurements were performed in the same group. However, the OC levels were reduced following RWL. In case of the males, the intake group after weight loss demonstrated a significant increase in BMD (p<0.05). Correlation analysis of the data for the male group showed significant correlations between serum OC and iron contents (p<0.05), total BMD and TIBC(total iron binding capacity) (p<0.05), and transferrin and iron concentrations (p<0.05). In the female group, serum OC and iron (p<0.01), transferrin and TIBC(total iron binding capacity) (p<0.01) showed correlations. In addition, between serum OC and ferritin (p<0.05), total BMD and ferritin (p<0.05), TIBC and iron (p<0.05) were shown to have some degree of correlation in the global evaluations.

This study examined the effects of an eight-week neuromuscular training (NMT) program on knee valgus angle in African American female athletes. Twenty-six female collegiate athletes participated. NMT group (n=15, 19.6±1.12 years) underwent an intervention training program that included three main components (plyometric and movement, core strengthening and balance, and resistance training). While, control group (n=11, 19.3±1.50 years) underwent the resistance training protocol for eight weeks. We hypothesized the NMT program would significantly decrease knee valgus angles during a drop vertical jump (DVJ) at landing for the NMT group when compared to the control group. Wilcoxon signed rank tests were done on the Pre-and Post-test findings. Results showed maximum valgus angle (VGmax) is significantly decreased (p<.05), and Maximum flexion (Flexmax) is significantly increased during the drop vertical jump in dominant leg (p<.05). The results support the hypothesis that an 8-week NMT program that combines injury prevention-training components can decrease an injury risk factor such as knee valgus in African American female athletes.

This study identifies factors affecting match results from major international competitions in women's handball in the last four years. The 12 countries that participated for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics were included in the analysis, and a total of 281 matches from 4 major international competitions were analyzed. To identify factors affecting winning and losing, independent sample t-test and logistic regression analysis were conducted on the variables present in the official records. The findings present several factors that have positive and negative effects on match results. In the analysis of differences in win and loss factors, 6m goals success rate, 9m success rate, FB goals and shooting, AS, BS, and ST had positive effects on winning. Logistic regression analysis had 84.5% accuracy. 6m and Wing goal, 9m success rate, FB shooting, GK Wing save rate, and GK 9m save rate increased the probability of winning.
Low back pain is prevalent in sport and the lumbar disc is a pain generator. Conservative care of these physically demanding patients is not consistent as outcome data has not established optimal strategies. Investigating disc injury mechanisms using experimental models will contribute to the creation of treatment strategies that will take into effect movements to avoid and minimize to reduce unwanted strain on the injured tissues throughout the recovery process. Additionally, how disc tissue acquires nutrition would help provide insight into activities that may facilitate the ability of disc tissue to sustain health and promote optimal healing. Rotational forces and compression in trunk-flexed positions may inflict injury to the annulus and endplate structures. Activity to facilitate nutrients through the endplate into the nucleus of the disc and restriction of exasperating movements may be effective in returning athletes to their desired levels of performance efficiently. The purpose of this review is to inquire possible disc injury mechanisms and how they occur in sport. It will also address recommendations for treatment interventions based on disc healing and metabolism evidence.
Purpose: We examined the associations between anaerobic power, maximal strength, and isokinetic strength in Korean National snowboarders. Methods: We examined cross-sectional associations between isokinetic trunk strength in 89 Korean National snowboarders (mean age: 22.17 ± 4.82 years). The main outcome measures were the Wingate anaerobic power test, maximal strength test, and isokinetic knee strength test. Results: Isokinetic trunk strength was correlated with anaerobic power (lower average power, peak power, and power-drop rate). Further, trunk strength flexion and extension were significantly associated with maximal strength (knee strength and one-repetition maximum). Conclusions: The Korean national snowboarders’ anaerobic capacity and maximal muscle strength measurements were positively associated with their isokinetic trunk strength. Further research is needed to elucidate the core balance and muscle-growth mechanisms underlying this association; ideally, future studies will involve exercise and treatment interventions to identify causal relationships.
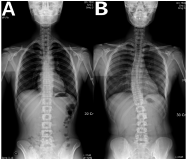
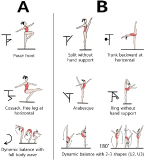
The study aimed to investigate the demographic and physical characteristics of South Korean female elite rhythmic gymnasts with scoliosis. Twenty-eight female elite rhythmic gymnasts aged 16.1 ±3.0 years were enrolled and divided by Cobb angle into a scoliosis group and a non-scoliosis group. In addition to the baseline characteristics of each group, visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for lumbago and results of the 36-item health survey version 2 (SF-36v2) questionnaires were collected. The pelvic tilt degree, leg length, hip range of motion and back-muscle strength were also measured and analyzed together. Radiographs of the thoracolumbar spine were taken for each subject. The scoliosis group (n=17) had significantly higher age, height, weight, and body fat compared to the non-scoliosis group. Further, six of the scoliosis group gymnasts had lumbar compression fractures or spondylolysis. Spinal flexors and extensors of all the subjects were balanced in strength but the lateral flexors showed noticeable imbalance. Elite rhythmic gymnasts were found to be increasingly susceptible to scoliosis and other spinal disorders with age and years of training. Spinal lateral-flexor muscle imbalance was more severe with scoliosis.

The purpose of this study was to compare judo-related physical fitness, body composition, and isokinetic knee functions of male judo athletes from different age groups. Subjects for this study were thirty male judo athletes and randomly divided into three groups: cadet judo athletes (CJA, n=10), junior judo athletes (JJA, n=10) and senior judo athletes (SJA, n=10). Body composition, physical fitness, anaerobic wingate test, and isokinetic knee strength test were analyzed for comparing characteristics of judo athletes with age. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA followed Scheffe post hoc test. As the result of this study, body weight and muscle mass were significantly higher in the SJA group than those in the CJA group. The SJA group had significantly higher sit-up, vertical jump, side step and sit-and-reach values than the CJA and JJA groups, and the JJA group had significantly higher sit-up and back strength values than the CJA group. The absolute values of peak power (PP) and average power (AP) and relative values of PP in the SJA group showed significant differences compared to the CJA and JJA groups. Therefore, present findings provided research evidence that anaerobic power, maximal muscle strength and endurance would positively regulate performance of judo athletes with increasing age and athletic experience. Coaches and trainers in the field should try to provide a periodic training program to improve judo-related physical fitness and succeed.
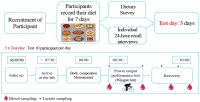
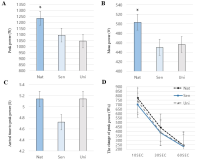
The aim of this study was to assess the eating habits of Korean wrestlers, and to explore the impact of differences in dietary intake on power output performance and blood lactate concentrations. Thirty adult wrestlers with more than seven years of experience each were included, grouped according to their competitive level (national, senior, and university team level). Participants recorded their dietary intake for seven days; nutritional analysis was performed using the CAN-Pro 4.0 software. After the nutritional survey, power output performance (Wingate test) was evaluated and blood parameters, including lactate concentration, were assessed. The wrestlers’ dietary assessments revealed differences in carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake among the groups, as well as differences in the peak power, mean power, and change in peak power, obtained from the Wingate test. Finally, the senior group had a significantly higher and lower lactate concentration than the university group immediately post training and 30 minutes post training, respectively. Follow-up studies should reveal more accurate associations between nutritional intake, nutritional quality, and performance. Finally, considering a study concerning nutrition and weight loss based on the results from this study, including not only wrestlers but also combat sport athletes will benefit nutrition education as well as athletes’ intake and performance.